Comprehensive analysis of PDE2A: a novel biomarker for prognostic value and immunotherapeutic potential in human cancers
- PMID: 39699377
- PMCID: PMC11653488
- DOI: 10.1590/1414-431X2024e14220
Comprehensive analysis of PDE2A: a novel biomarker for prognostic value and immunotherapeutic potential in human cancers
Abstract
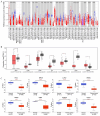
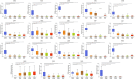
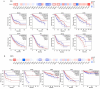
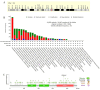
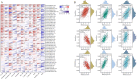
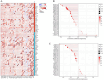
Phosphodiesterase 2A (PDE2A) plays a pivotal role in modulating cyclic nucleotide metabolism. Recent studies have shown that PDE2A is associated with some tumors, but its expression profiles, prognostic significance, and immunological roles in diverse cancer types remain unclear. Utilizing advanced bioinformatics tools, we performed a comprehensive analysis of PDE2A gene expression in multiple human cancers. Our study revealed that PDE2A expression was significantly reduced in the majority of cancer types and clinicopathological stages (I to IV) compared to normal tissues. Additionally, PDE2A expression was closely related to the prognosis of cancers such as stomach adenocarcinoma (STAD), ovarian serous cystadenocarcinoma (OV), and liver hepatocellular carcinoma (LIHC). Cox regression analyses indicated that PDE2A can act as an independent prognostic factor for these cancers. The level of PDE2A DNA methylation was significantly decreased in most cancers. Genetic alterations in PDE2A predominantly manifest in the form of amplifications. Moreover, infiltrating cells and immune checkpoint genes, including PDCD1, exhibited notable correlations with PDE2A expression. Significant associations were observed between PDE2A expression and tumor mutation burden as well as microsatellite instability. Single cell sequencing revealed PDE2A's crucial role in regulating differentiation and angiogenesis of cancer cells. Functional enrichment analysis emphasized the important role of PDE2A in synaptic transmission and tumor development. Aberrant expression of PDE2A influenced the sensitivity of various antitumor and chemotherapy drugs. This research provided a comprehensive analysis of PDE2A in human cancers, highlighting its potential as both a prognostic marker and an immunotherapy target for future research.
Figures



References
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

