Exploring the mechanism of berberine treatment for atherosclerosis combined with non-alcoholic fatty liver disease based on bioinformatic and experimental study
- PMID: 39700090
- PMCID: PMC11658604
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0314961
Exploring the mechanism of berberine treatment for atherosclerosis combined with non-alcoholic fatty liver disease based on bioinformatic and experimental study
Abstract
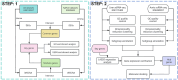
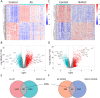
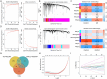
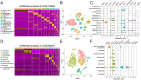
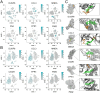
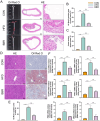
Atherosclerosis (AS) and Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) are chronic metabolic disorders with high prevalence and significant health impacts. Both conditions share common pathophysiological pathways including abnormal lipid metabolism and inflammation. Berberine (BBR), an isoquinoline alkaloid, is known for its beneficial effects on various metabolic and cardiovascular disorders. This study investigates BBR's impact on AS and NAFLD through bioinformatics analysis and experimental models. This study utilized various bioinformatics methods, including transcriptome analysis, weighted gene co-expression network analysis (WGCNA), machine learning, and molecular docking, to identify key genes and pathways involved in AS and NAFLD. Subsequently an animal model of AS combined with NAFLD was established using ApoE-/- mice fed a high-fat diet. The efficacy and mechanism of action of BBR were verified using methods such as hematoxylin and eosin (HE) staining, Oil Red O staining, and real-time quantitative PCR (RTqPCR). Through transcriptome analysis, WGCNA, and machine learning, this study identified 48 key genes involved in both AS and NAFLD. Function analysis revealed that the implicated genes were significantly involved in pathways like cytokine-cytokine receptor interaction, chemokine signaling, and IL-17 signaling pathway, suggesting their role in inflammation and immune responses. Single cell validation identified six key genes: dual specificity phosphatase 6 (DUSP6), chemokine ligand 3 (CCL3), complement component 5a receptor 1 (C5AR1), formyl peptide receptor 1 (FPR1), myeloid nuclear differentiation antigen (MNDA), and proviral integration site of murine 2(PIM2). Finally, molecular docking and animal experiments showed that BBR significantly reduced lipid deposits and inflammatory markers in liver and aortic tissues. In conclusion, BBR can improve AS combined with NAFLD by regulating genes like MNDA, PIM2, DUSP6, CCL3, C5AR1, and FPR1, with the mechanism related to inflammation control. The findings suggest potential clinical benefits of BBR in reducing the progression of both AS and NAFLD, warranting further investigation.
Copyright: © 2024 Wang et al. This is an open access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original author and source are credited.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures
References
-
- Ampuero J, Gallego-Duran R, Romero-Gomez M. Association of NAFLD with subclinical atherosclerosis and coronary-artery disease: meta-analysis. Rev Esp Enferm Dig. 2015;107(1):10–6. . - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

