Using Electronic Health Records to Identify the Daily Primary Provider During Hospitalization
- PMID: 39700341
- PMCID: PMC11661743
- DOI: 10.1097/CCE.0000000000001189
Using Electronic Health Records to Identify the Daily Primary Provider During Hospitalization
Abstract
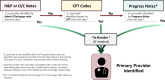
Objectives: Providers vary in their impact on clinical outcomes, but this is rarely accounted for in healthcare research. By failing to identify the provider responsible for a patient's care, investigators miss an opportunity to account for nonrandom variation in outcomes. Prior methods of identifying responsible providers have relied on manual chart review, which is time-consuming and expensive, or analysis of claims data, which has been demonstrated to be inaccurate. To address these gaps, we sought to develop an algorithm using electronic health record (EHR) data to identify the responsible provider for each day of a patient's hospitalization.
Design: A multicenter retrospective cohort study.
Setting: Midwest healthcare system.
Patients: Hospitalized patients and their providers.
Interventions: None.
Measurements and main results: We first confirmed high inter-rater reliability of manual chart review to identify the responsible provider. Using manual chart review as the gold standard, we then assessed the accuracy of an automated algorithm in a set of randomly selected patients. The agreement between two independent physicians in their determination of the responsible provider by chart review was 100%. Among 200 randomly selected patients, the algorithm identified the same responsible provider as the physician chart reviewer on 93% (3372/3626; 95% CI, 92-94%) of patient-days.
Conclusions: Readily available EHR data can be used to assign patients to providers daily with a high degree of accuracy. This methodology could be applied in healthcare research to identify sources of variation other than the intervention being studied.
Copyright © 2024 The Authors. Published by Wolters Kluwer Health, Inc. on behalf of the Society of Critical Care Medicine.
Conflict of interest statement
Dr. Ingraham is supported by the National Institutes of Health (NIH)/National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute (NHLBI; K23 HL166783). Dr. Kohn is supported by the NIH/NHLBI (K23 HL146894). Dr. Kerlin is supported by the NIH/NHLBI (R01 HL146386). The remaining authors have disclosed that they do not have any potential conflicts of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Kahn JM, Goss CH, Heagerty PJ, et al. : Hospital volume and the outcomes of mechanical ventilation. N Engl J Med 2006; 355:41–50 - PubMed
-
- Ingraham NE, Vakayil V, Pendleton KM, et al. : Recent trends in admission diagnosis and related mortality in the medically critically ill. J Intensive Care Med 2022; 37:185–194 - PubMed
-
- Amaravadi RK, Dimick JB, Pronovost PJ, et al. : ICU nurse-to-patient ratio is associated with complications and resource use after esophagectomy. Intensive Care Med 2000; 26:1857–1862 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources