HDAC6 inhibitor-loaded brain-targeted nanocarrier-mediated neuroprotection in methamphetamine-driven Parkinson's disease
- PMID: 39700694
- PMCID: PMC11722933
- DOI: 10.1016/j.redox.2024.103457
HDAC6 inhibitor-loaded brain-targeted nanocarrier-mediated neuroprotection in methamphetamine-driven Parkinson's disease
Abstract
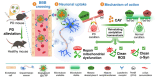
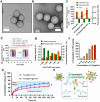
The dynamic equilibrium between acetylation and deacetylation is vital for cellular homeostasis. Parkinson's disease (PD), a neurodegenerative disorder marked by α-synuclein (α-syn) accumulation and dopaminergic neuron loss in the substantia nigra, is associated with a disruption of this balance. Therefore, correcting this imbalance with histone deacetylase (HDAC) inhibitors represents a promising treatment strategy for PD. CAY10603 (CAY) is a potent and selective HDAC6 inhibitor. However, because of its poor water solubility and short biological half-life, it faces clinical limitations. Herein, we engineered lactoferrin-decorated CAY-loaded poly(lactic-co-glycolic acid) nanoparticles (denoted as PLGA@CAY@Lf NPs) to effectively counter methamphetamine (Meth)-induced PD. PLGA@CAY@Lf NPs showed enhanced blood-brain barrier crossing and significant brain accumulation. Notably, CAY released from PLGA@CAY@Lf NPs restored the disrupted acetylation balance in PD, resulting in neuroprotection by reversing mitochondrial dysfunction, suppressing reactive oxygen species, and inhibiting α-syn accumulation. Additionally, PLGA@CAY@Lf NPs treatment normalized dopamine and tyrosine hydroxylase levels, reduced neuroinflammation, and improved behavioral impairments. These findings underscore the potential of PLGA@CAY@Lf NPs in treating Meth-induced PD and suggest that an innovative HDAC6-inhibitor-based strategy can be used to treat PD.
Keywords: CAY10603; HDAC6 inhibitor; Lactoferrin; PLGA nanoparticle; Parkinson's disease.
Copyright © 2024 The Authors. Published by Elsevier B.V. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of competing interest The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Figures








References
-
- Wu J., Cui X., Ke P.C., Mortimer M., Wang X., Bao L., Chen C. Nanomaterials as novel agents for amelioration of Parkinson's disease. Nano Today. 2021;41
-
- V Kalia L., Lang A.E. Parkinson's disease. Lancet. 2015;386:896–912. - PubMed
-
- Liu J., Liu C., Zhang J., Zhang Y., Liu K., Song J.-X., Sreenivasmurthy S.G., Wang Z., Shi Y., Chu C., Zhang Y., Wu C., Deng X., Liu X., Song J., Zhuang R., Huang S., Zhang P., Li M., Wen L., wu Zhang Y., Liu G. A self-assembled α-synuclein nanoscavenger for Parkinson's disease. ACS Nano. 2020;14:1533–1549. - PubMed
-
- Morris H.R., Spillantini M.G., Sue C.M., Williams-Gray C.H. The pathogenesis of Parkinson's disease. Lancet. 2024;403:293–304. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

