Liver X Receptors and Inflammatory-Induced C/EBPβ Selectively Cooperate to Control CD38 Transcription
- PMID: 39701049
- PMCID: PMC11781815
- DOI: 10.1159/000543274
Liver X Receptors and Inflammatory-Induced C/EBPβ Selectively Cooperate to Control CD38 Transcription
Abstract
Introduction: Macrophages abundantly express liver X receptors (LXRs), which are ligand-dependent transcription factors and sensors of several cholesterol metabolites. In response to agonists, LXRs promote the expression of key lipid homeostasis regulators. Cross talk between LXRs and inflammatory signals exists in a cell type- and gene-specific manner. A common feature in the macrophage response to inflammatory mediators is the induction of CCAAT/enhancer-binding protein beta (C/EBPβ), a master transcriptional regulator and lineage-determining transcription factor in monocytes/macrophages.
Methods: Quantitative real-time PCR in control and C/EBPβ-deficient macrophages was used to explore the role of C/EBPβ in the cross talk between inflammatory mediators and the macrophage response to pharmacological LXR activation. The functional interaction between C/EBPβ and LXRs on selected genomic regions was further characterized by chromatin-immunoprecipitation (ChIP) and gene reporter studies.
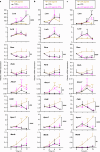
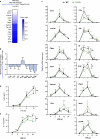
Results: Whereas inflammatory signaling repressed several LXR-regulated genes involved in lipid metabolism, these effects were conserved after deletion of C/EBPβ. In contrast, inflammatory mediators and LXRs synergistically induced the expression of the multifunctional protein CD38 in a C/EBPβ-dependent manner. C/EBPβ and LXRs bound to several regions with enhancer activity upstream and within the mouse Cd38 gene and their functional cooperation in macrophages required intact binding sites for LXR and C/EBPβ.
Conclusion: This study reveals positive cross talk between C/EBPβ and LXRs during the macrophage inflammatory response, which selectively impacts CD38 expression.
Keywords: CCAAT/enhancer-binding protein beta; CD38; Interferon gamma; Lipopolysaccharide; Liver X receptor; Macrophage; Tumor necrosis factor alpha.
© 2024 The Author(s). Published by S. Karger AG, Basel.
Conflict of interest statement
E.G. is currently an employee at OneChain Immunotherapeutics. J.M. is currently an employee at Avidity Biosciences. E.N.C. holds a patent on the use of CD38 inhibitors for metabolic diseases that is licensed by Elysium Health. E.N.C. is a consultant for TeneoBio, Calico, Mitobridge, and Cytokinetics. E.N.C. is on the advisory board of Eolo Pharma. E.N.C. owns stocks in TeneoBio. Dr. Chini is the head of the external research advisory board for Neolaia Bio. Research in the Chini laboratory has been conducted in compliance with the Mayo Clinic conflict of interest policies. C.C. is a consultant for Aromics. The rest of the authors declare no potential conflicts of interest.
Figures






References
-
- Okabe Y, Medzhitov R. Tissue biology perspective on macrophages. Nat Immunol. 2016;17(1):9–17. - PubMed
-
- A-González N, Castrillo A. Liver X receptors as regulators of macrophage inflammatory and metabolic pathways. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2011;1812(8):982–94. - PubMed
-
- Hu X, Li S, Wu J, Xia C, Lala DS. Liver X receptors interact with corepressors to regulate gene expression. Mol Endocrinol. 2003;17(6):1019–26. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

