Age- and Sex-Related Volumetric Density Differences in Trabecular and Cortical Bone of the Proximal Femur in Healthy Population
- PMID: 39701108
- PMCID: PMC11658838
- DOI: 10.11005/jbm.24.765
Age- and Sex-Related Volumetric Density Differences in Trabecular and Cortical Bone of the Proximal Femur in Healthy Population
Abstract
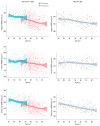
Background: There are age- and sex-related increases in the prevalence of osteoporosis. Bone densitometry based on dual energy X-ray absorptiometry (DXA) is the gold standard for the assessment of bone mineral density (BMD). Three-dimensional (3D) analysis of the proximal femur (3D-DXA) allows discrimination between cortical and trabecular compartments, and it has shown a good correlation with computed tomography. We aimed to assess age- and sex-related volumetric density differences in trabecular and cortical bone using 3D-DXA and determine the reference intervals for integral volumetric (v)BMD within the Argentine population.
Methods: Healthy female and male adult subjects (N=1,354) from Argentina were included. Hip BMD was measured using DXA, and 3D analysis was performed using 3D-Shaper software. The integral vBMD, cortical surface BMD, and trabecular vBMD (trab vBMD) were measured.
Results: The study population included 73.9% women (N=1,001) and 26.13% men (N=353). We found a significant decrease in integral vBMD between 20 and 90 years in both sexes (women, -23.1%; men, -16.6%). Bone loss indicated in the integral vBMD results was mainly due to a decrease in trabecular bone in both sexes (women, -33.4%; men, -27.7%). The age-related loss of cortical bone density was less and was limited to the female population, without no age-related differences in men. Moreover, 3D-DXA allowed us to propose reference intervals for integral vBMD.
Conclusions: We found age- and sex-related bone loss between 20 and 90 years in an Argentine cohort via integral vBMD measurements using 3D-DXA, mainly due to decreases in trabecular bone in both sexes. The age-related loss of cortical bone density was less and was limited to the female population.
Keywords: 3D-DXA; Bone and bones; Bone density; Cancellous bone; Cortical bone.
Conflict of interest statement
No potential conflict of interest relevant to this article was reported.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Effects of osteoporosis drug treatments on cortical and trabecular bone in the femur using DXA-based 3D modeling.Osteoporos Int. 2018 Oct;29(10):2323-2333. doi: 10.1007/s00198-018-4624-4. Epub 2018 Jul 4. Osteoporos Int. 2018. PMID: 29974136
-
Alteration of Volumetric Bone Mineral Density Parameters in Men with Spinal Cord Injury.Calcif Tissue Int. 2023 Sep;113(3):304-316. doi: 10.1007/s00223-023-01110-2. Epub 2023 Jun 23. Calcif Tissue Int. 2023. PMID: 37353625
-
Bone Analysis Using Trabecular Bone Score and Dual-Energy X-Ray Absorptiometry-Based 3-Dimensional Modeling in Postmenopausal Women With Primary Hyperparathyroidism.Endocr Pract. 2022 Jan;28(1):83-89. doi: 10.1016/j.eprac.2021.08.006. Epub 2021 Aug 25. Endocr Pract. 2022. PMID: 34450273
-
Analysis of the evolution of cortical and trabecular bone compartments in the proximal femur after spinal cord injury by 3D-DXA.Osteoporos Int. 2018 Jan;29(1):201-209. doi: 10.1007/s00198-017-4268-9. Epub 2017 Oct 17. Osteoporos Int. 2018. PMID: 29043391
-
Volumetric BMD by 3D-DXA and Trabecular Bone Score in Adults With Down Syndrome.J Clin Densitom. 2021 Oct-Dec;24(4):630-637. doi: 10.1016/j.jocd.2021.01.010. Epub 2021 Jan 30. J Clin Densitom. 2021. PMID: 33618949 Review.
Cited by
-
Positive Effect of Yerba Mate (Ilex paraguariensis) Consumption on Bone Mineral Density in Postmenopausal Women Assessed by Dual Energy X-Ray Absorptiometry-Based 3-Dimensional Modeling.J Bone Metab. 2025 May;32(2):123-132. doi: 10.11005/jbm.24.827. Epub 2025 May 31. J Bone Metab. 2025. PMID: 40537107 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Hui SL, Johnston CC, Jr, Mazess RB. Bone mass in normal children and young adults. Growth. 1985;49:34–43. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources