Cerebral blood flow and arterial responses in migraine: history and future perspectives
- PMID: 39701954
- PMCID: PMC11656563
- DOI: 10.1186/s10194-024-01903-2
Cerebral blood flow and arterial responses in migraine: history and future perspectives
Abstract
Introduction: It is largely accepted that migraine with aura (MA) is caused by cortical spreading depression (CSD) and that migraine without aura (MO) is not. This is mostly based on old studies of regional cerebral blood flow (rCBF) and studies of vascular responses. These studies are partly forgotten today and may, therefore, be worthwhile reviewing.
Methods: The review is based on the authors life-long involvement in these issues and his knowledge of the relevant literature plus scrutiny of reference lists of these papers.
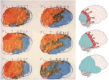
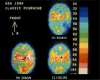
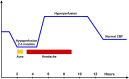
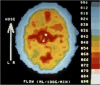
Results: The strongest evidence for CSD in MA came from studies using intraarterial injection of 133-Xenon and recording from 254 areas of the relevant hemisphere. Measurements could be taken before and during development of an attack because the procedure triggered MA. The findings were identical to many features of CSD. They were confirmed using 133-Xenon Single Photon Emission Computerized Tomography (SPECT).It was shown that the generally accepted vasospastic theory of migraine was incorrect. Headache started while rCBF was decreased and did not change during later hyperperfusion. rCBF remained normal in MO but later studies have shown increase in areas also activated by other pain. Flow Was focally increased in the brain stem also after treatment of the pain. Dilatation of large cerebral arteries during MO attack was first shown with ultrasound and later confirmed by MR angiography which also showed a lack of dilatation of extracerebral arteries.
Discussion: Much has in later years been done using modern PET and MR techniques. These studies have confirmed the old studies and have added many new aspects which are not reviewed here. The final proof of CSD during MA and its absence during MO still awaits the definitive study.
Conclusion: Studies from the 1980ies and 1990ies caused a fundamental shift in our understanding of the vascular and cortical mechanisms of migraine. They remain a solid base for our current understanding and inspire further study.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Declarations. Competing interests: JO owns stock in Novo, Lundbeck, Moberg Pharma and Cephagenix.
Figures
Similar articles
-
History of migraine with aura and cortical spreading depression from 1941 and onwards.Cephalalgia. 2010 Jul;30(7):780-92. doi: 10.1111/j.1468-2982.2009.02015.x. Cephalalgia. 2010. PMID: 19740119 Review.
-
Cerebral and extracranial circulatory disturbances in migraine: pathophysiological implications.Cerebrovasc Brain Metab Rev. 1991 Spring;3(1):1-28. Cerebrovasc Brain Metab Rev. 1991. PMID: 2036298
-
Cerebral blood flow in migraine with aura.Pathol Biol (Paris). 1992 Apr;40(4):318-24. Pathol Biol (Paris). 1992. PMID: 1495815 Review.
-
[Cerebral blood flow in migraine without aura].Pathol Biol (Paris). 1992 Apr;40(4):325-31. Pathol Biol (Paris). 1992. PMID: 1495816 Review. French.
-
Cortical spreading depression and estrogen.Headache. 2007 Sep;47 Suppl 2:S79-85. doi: 10.1111/j.1526-4610.2007.00818.x. Headache. 2007. PMID: 17850538 Review.
Cited by
-
Neurovascular coupling dysfunction in encephalopathy: pathophysiological advances and clinical implications.Front Neurol. 2025 May 20;16:1522485. doi: 10.3389/fneur.2025.1522485. eCollection 2025. Front Neurol. 2025. PMID: 40463938 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Schiller F (1975) The migraine tradition. Bull Hist Med 49:1–19 - PubMed
-
- Wolff HG (1963) Headache and other head pain, 2nd edn. Oxford University Press
-
- Olesen J, Burstein R, Ashina M et al (2009) Origin of pain in migraine: evidence for peripheral sensitisation. Lancet Neurol 8:679–690 - PubMed
-
- Olesen J, Friberg L, Olsen TS et al (1990) Timing and topography of cerebral blood flow, aura, and headache during migraine attacks. Ann Neurol 28:791–798 - PubMed
-
- Lauritzen M, Olesen J (1984) Regional cerebral blood flow during migraine attacks by Xenon-133 inhalation and emission tomography. Brain 107(Pt 2):447–461 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

