Identification and validation of differentially expressed disulfidptosis-related genes in hypertrophic cardiomyopathy
- PMID: 39701955
- PMCID: PMC11660498
- DOI: 10.1186/s10020-024-01024-1
Identification and validation of differentially expressed disulfidptosis-related genes in hypertrophic cardiomyopathy
Abstract
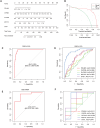
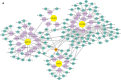
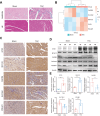
Hypertrophic cardiomyopathy (HCM) is one of the most common cardiovascular diseases with no effective treatment due to its complex pathogenesis. A novel cell death, disulfidptosis, has been extensively studied in the cancer field but rarely in cardiovascular diseases. This study revealed the potential relationship between disulfidptosis and hypertrophic cardiomyopathy and put forward a predictive model containing disulfidptosis-associated genes (DRGs) of GYS1, MYH10, PDMIL1, SLC3A2, CAPZB, showing excellent performance by SVM machine learning model. The results were further validated by western blot, RNA sequencing and immunohistochemistry in a TAC mice model. In addition, resveratrol was selected as a therapeutic drug targeting core genes using the CTD database. In summary, this study provides new perspectives for exploring disulfidptosis-related biomarkers and potential therapeutic targets for hypertrophic cardiomyopathy.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Declarations. Ethics approval and consent to participate: All animal experiments were performed with the approval of the Institutional Animal Care and Use Committee of the Fourth Affiliated Hospital of Soochow University (2400321). Consent for publication: Not applicable. Competing interests: The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
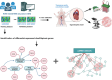
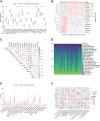
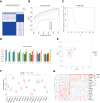
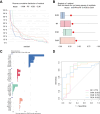

References
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- KJXW2023086/Suzhou Science and Education Youth Science and Technology Project
- 82403624/National Natural Science Foundation of China
- 81873486/National Natural Science Foundation of China
- BK20240637/Natural Science Foundation of Jiangsu Province
- AHWJ2022c008/Anhui provincial health research project
- 202304295107020117/Anhui clinical medical research transformation project
- BE2022754/Science and Technology Development Program of Jiangsu Province-Clinical Frontier Technology
- SZYQTD202102/Clinical Medicine Expert Team (Class A) of Jinji Lake Health Talents Program of Suzhou Industrial Park
- SZXK202129/Suzhou Key Discipline for Medicine
- SKY2021002/Demonstration of Scientific and Technological Innovation Project
- LCZX202132/Suzhou Dedicated Project on Diagnosis and Treatment Technology of Major Diseases
- SZS2023021/Suzhou Key Laboratory of Diagnosis and Treatment of Panvascular Diseases
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

