Cardiac findings in a phase II double-blind randomized placebo-controlled trial of combination therapy (HAZDPac) to treat COVID-19 patients
- PMID: 39702045
- PMCID: PMC11657509
- DOI: 10.1186/s12872-024-04376-y
Cardiac findings in a phase II double-blind randomized placebo-controlled trial of combination therapy (HAZDPac) to treat COVID-19 patients
Retraction in
-
Retraction Note: Cardiac findings in a phase II double-blind randomized placebo-controlled trial of combination therapy (HAZDPac) to treat COVID-19 patients.BMC Cardiovasc Disord. 2025 Feb 18;25(1):112. doi: 10.1186/s12872-025-04554-6. BMC Cardiovasc Disord. 2025. PMID: 39966704 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Abstract
Objective: Hydroxychloroquine paired with Azithromycin, Vitamin C, Vitamin D, and Zinc (HAZDPac), was used as a multidrug therapy method to treat COVID-19 illness and superimposed secondary bacterial pneumonia. Concerns have been raised though about such combinations regarding cardiac QTc interval prolongation and risks of arrhythmias, which we set out to address in this study.
Design: We evaluated cardiac safety in a Phase II Double-Blind Randomized Placebo-Controlled Trial of Combination Therapy to Treat COVID-19 Infections study, conducted by ProgenaBiome. Acutely ill patients with COVID-19 had QTc intervals recorded in an outpatient setting utilizing a continuously worn EKG monitor for the duration of the 10 days treatment. QTc intervals were normally distributed. Two-sample t-tests were used to measure any significant differences in QTc intervals between treatment and placebo groups.
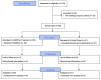
Results: Between March 2020 and June 2021, 118 COVID-19 patients were recruited and signed informed consent, of which 83 were enrolled for a Double-Blind Randomized Placebo-Controlled Trial. Of the 83, 52 patients were randomly assigned to receive HAZDPac treatment, and 31 patients to receive placebo. Overall, and in stratified analysis by gender, maximum QTc values of patients in the treatment arm were normal and no differences were observed when compared to maximum QTc values from patients in the placebo arm (p ≥ 0.15). There were no adverse events related to HAZDPac treatment.
Conclusion: We found that the outpatient treatment of COVID-19 patients with HAZDPac which includes Hydroxychloroquine and Azithromycin, was not associated with prolongation of QTc compared to placebo and QTc remained within normal range.
Clinical trial: Clinical Trial NCT04482686, clinicaltrials.gov, date of registration 07/21/2020.
Keywords: Azithromycin; COVID-19; Hydroxychloroquine; QTc interval; Safety.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Declarations. Ethics approval and consent to participate: This study involves human participants, and the study protocol was reviewed and approved by The Salus Institutional Review Board, Protocol #20071 and registered at Clinicaltrials.gov, Identifier NCT04482686. Participants gave informed consent to participate in the study before taking part. Consent for publication: All authors gave consent for publication. Participants gave written informed consent for their unidentified personal or clinical details along with any images to be published in this study. Competing interests: Dr Hazan is the CEO of Progenabiome, LLC and owns the Microbiome Research Foundation. Dr. McCullough owns the McCullough Foundation. Disclosures: Dr Hazan is the CEO of Progenabiome, LLC and owns the Microbiome Research Foundation. Dr. McCullough owns the McCullough Foundation.
Figures
References
-
- WHO. Transmission of SARS-CoV-2: implications for infection prevention precautions. 2020.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical