An overview of patients with intertrochanteric femoral fractures treated with proximal femoral nail fixation using important criteria
- PMID: 39702170
- PMCID: PMC11660553
- DOI: 10.1186/s12891-024-08197-0
An overview of patients with intertrochanteric femoral fractures treated with proximal femoral nail fixation using important criteria
Abstract
Background: This study aimed to assess important criteria, including osteoporosis, fracture type, implant position within the bone, fracture reduction, and radiographic union, in patients with intertrochanteric femoral fractures treated with proximal femoral nail (PFN) fixation and to show their effect on clinical outcomes.
Methods: PFN fixation was applied in 73 patients (41 females, 32 males; mean age: 64.5 ± 6.2). The T score, fracture type according to the AO Foundation and Orthopedic Trauma Association (AO/OTA), implant-related complications (IRCs), Harris hip score (HHS), Jensen social function (JSF) score, and Parker-Palmer mobility score (PPMS), postoperative reduction classification, screw position according to the Cleveland zone, Radiographic Union Scale for the Hip (RUSH) score, and tip-apex distance (TAD) were recorded.
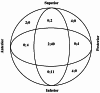
Results: Most screws were in central-central (n = 42) and inferior-central (n = 11) positions. IRCs were seen mostly in cases of screws placed in peripheral zones (n = 10) and were not observed in almost any patient with a TAD ≤ 25 mm (n = 52) (p < 0.001). Most of the patients with acceptable or good fracture reduction did not have IRCs (n = 11 and 50, respectively) (p < 0.001). Half of type 3A1 (n = 13) and most type 3A2 (n = 20) fractures showed radiographic union at 3 months, and most type 3A3 (n = 9) fractures showed radiographic union at 5 months (p < 0.05). At 12 months, type 3A2 fractures had the highest HHS (79.2 ± 5.3) and PPMS (3.9 ± 1.5), while type 3A3 fractures had the lowest HHS (70.3 ± 4.6) and PPMS (0.6 ± 2.8) (p < 0.05). At 12 and 24 months, type 3A3 fractures had higher JSF scores (2.8 ± 0.4 and 3.5 ± 0.5, respectively); at 3 months, type 3A1 fractures had higher JSF scores (3.1 ± 0.3) (p < 0.05). The radiographic bone union time was prolonged in patients with a T score ≤ -2.5 standard deviation (SD) (p < 0.05). The HHS and PPMS increased while the RUSH score, considered as the radiographic union, was going towards the 4th month and decreased after the 4th month (p < 0.05).
Conclusions: Considering the criteria (osteoporosis, fracture type, implant position within the bone, fracture reduction, and radiographic union) examined in this study, satisfactory results can be obtained with PFN fixation in the treatment of patients with intertrochanteric femoral fractures.
Keywords: Cleveland zone; Functional scores; Intertrochanteric femoral fracture; Postoperative reduction classification; Radiographic union scale for the hip; Tip-apex distance.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Declarations. Ethics approval and consent to participate: The research follows the basic principles of the Declaration of Helsinki, the study protocol was approved by the Ethics committee of Istinye University (No. 3/2022.K-20), and all individuals signed informed consent when participating in this study. Consent for publication: Not applicable. Competing interests: The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures


References
-
- Takigami I, Matsumoto K, Ohara A, Yamanaka K, Naganawa T, Ohashi M, et al. Treatment of trochanteric fractures with the PFNA (proximal femoral nail antirotation) nail system-report of early results. Bull NYU Hosp Jt Dis. 2008;66:276–9. - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

