Reliability of high-quantity human brain organoids for modeling microcephaly, glioma invasion and drug screening
- PMID: 39702477
- PMCID: PMC11659410
- DOI: 10.1038/s41467-024-55226-6
Reliability of high-quantity human brain organoids for modeling microcephaly, glioma invasion and drug screening
Erratum in
-
Author Correction: Reliability of high-quantity human brain organoids for modeling microcephaly, glioma invasion and drug screening.Nat Commun. 2025 Feb 4;16(1):1366. doi: 10.1038/s41467-025-56677-1. Nat Commun. 2025. PMID: 39905094 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Abstract
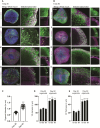
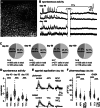
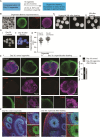
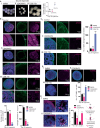
Brain organoids offer unprecedented insights into brain development and disease modeling and hold promise for drug screening. Significant hindrances, however, are morphological and cellular heterogeneity, inter-organoid size differences, cellular stress, and poor reproducibility. Here, we describe a method that reproducibly generates thousands of organoids across multiple hiPSC lines. These High Quantity brain organoids (Hi-Q brain organoids) exhibit reproducible cytoarchitecture, cell diversity, and functionality, are free from ectopically active cellular stress pathways, and allow cryopreservation and re-culturing. Patient-derived Hi-Q brain organoids recapitulate distinct forms of developmental defects: primary microcephaly due to a mutation in CDK5RAP2 and progeria-associated defects of Cockayne syndrome. Hi-Q brain organoids displayed a reproducible invasion pattern for a given patient-derived glioma cell line. This enabled a medium-throughput drug screen to identify Selumetinib and Fulvestrant, as inhibitors of glioma invasion in vivo. Thus, the Hi-Q approach can easily be adapted to reliably harness brain organoids' application for personalized neurogenetic disease modeling and drug discovery.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests: The authors (A.R., J.G., and E.G.) have filed an international patent related to the methodology and applications (Ref: PCT/EP2021/080414). J.G. and E.G. are co-founders of NeuronFab GmbH. All other authors declare no competing interests.
Figures



Comment in
-
Human brain organoids identify glioma inhibitors.Nat Rev Drug Discov. 2025 Feb;24(2):91. doi: 10.1038/d41573-025-00007-z. Nat Rev Drug Discov. 2025. PMID: 39794506 No abstract available.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
Grants and funding
- 70114276/Deutsche Krebshilfe (German Cancer Aid)
- 10.20.2.031MN/Fritz Thyssen Stiftung (Fritz Thyssen Foundation)
- VIP+ (03VP10540)/Bundesministerium für Bildung und Forschung (Federal Ministry of Education and Research)
- Project-ID 503306912 - FOR5547/Deutsche Forschungsgemeinschaft (German Research Foundation)
- SPP2127 GO 2301/5-2/Deutsche Forschungsgemeinschaft (German Research Foundation)
- RU 2795 ("Synapses under Stress"), Ro2327/13-2/Deutsche Forschungsgemeinschaft (German Research Foundation)
- BU 2974/3-2 - SPP2127, EXC-2151-390873048-Cluster of Excellence- ImmunoSensation2/Deutsche Forschungsgemeinschaft (German Research Foundation)
- Freigeist-A110720/Volkswagen Foundation (VolkswagenStiftung)

