PP2C phosphatases-terminators of suicidal thoughts
- PMID: 39702569
- PMCID: PMC11659304
- DOI: 10.1038/s41419-024-07269-2
PP2C phosphatases-terminators of suicidal thoughts
Abstract
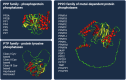
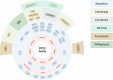
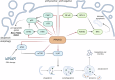
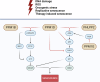
Cell death and related signaling pathways are essential during development and in various physiological and pathological conditions. Post-translational modifications such as ubiquitination and phosphorylation play an important role in these signaling pathways. The involvement of kinases - enzymes that catalyze protein phosphorylation - in cell death signaling has been extensively studied. On the other hand, not many studies have been devoted to analyzing the role in cell death of phosphatases, enzymes involved in the removal of phosphorylated residues added to proteins by kinases. Obviously, the two opposite reactions, phosphorylation and dephosphorylation, are equally important in the regulation of protein functions and subsequently in the execution of the cell death program. Here, we have summarized recent work on the involvement of serine-threonine PP2C phosphatases in cell death pathways, senescence and autophagy, focusing in particular on the most studied phosphatase PPM1D (PP2Cδ) as an example of the regulatory role of PP2Cs in cell death. The review should help to draw attention to the importance of PP2C family phosphatases in cell death checkpoints and to discover new targets for drug development.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests: The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
References
-
- Lammers T, Lavi S. Role of type 2C protein phosphatases in growth regulation and in cellular stress signaling. Crit Rev Biochem Mol Biol. 2007;42:437–61. - PubMed
-
- Lu G, Wang Y. Functional diversity of mammalian type 2c protein phosphatase isoforms: new tales from an old family. Clin Exp Pharmacol Physiol. 2008;35:107–12. - PubMed
-
- Neumann J, Boknik P, Kirchhefer U, Gergs U. The role of PP5 and PP2C in cardiac health and disease. Cell Signal. 2021;85:110035. - PubMed
-
- Tong Y, Quirion R, Shen SH. Cloning and characterization of a novel mammalian PP2C isozyme. J Biol Chem. 1998;273:35282–90. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

