Myoblast-derived ADAMTS-like 2 promotes skeletal muscle regeneration after injury
- PMID: 39702607
- PMCID: PMC11659564
- DOI: 10.1038/s41536-024-00383-x
Myoblast-derived ADAMTS-like 2 promotes skeletal muscle regeneration after injury
Abstract
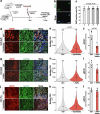
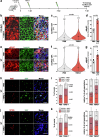
Skeletal muscle regeneration and functional recovery after minor injuries requires the activation of muscle-resident myogenic muscle stem cells (i.e. satellite cells) and their subsequent differentiation into myoblasts, myocytes, and ultimately myofibers. We recently identified secreted ADAMTS-like 2 (ADAMTSL2) as a pro-myogenic regulator of muscle development, where it promoted myoblast differentiation. Since myoblast differentiation is a key process in skeletal muscle regeneration, we here examined the role of ADAMTSL2 during muscle regeneration after BaCl2 injury. Specifically, we found that muscle regeneration was delayed after ablation of ADAMTSL2 in myogenic precursor cells and accelerated following injection of pro-myogenic ADAMTSL2 protein domains. Mechanistically, ADAMTSL2 regulated the number of committed myoblasts, which are the precursors for myocytes and regenerating myofibers. Collectively, our data support a role for myoblast-derived ADAMTSL2 as a positive regulator of muscle regeneration and provide a proof-of-concept for potential therapeutic applications.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests: The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures





References
Grants and funding
- R01 AR080616/AR/NIAMS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AR078857/AR/NIAMS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AR080096/AR/NIAMS NIH HHS/United States
- R01AR070748/U.S. Department of Health & Human Services | NIH | National Institute of Arthritis and Musculoskeletal and Skin Diseases (NIAMS)
- R01 AR070748/AR/NIAMS NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

