Emerging Therapeutics in the Fight Against EV-D68: A Review of Current Strategies
- PMID: 39702696
- PMCID: PMC11659119
- DOI: 10.1111/irv.70064
Emerging Therapeutics in the Fight Against EV-D68: A Review of Current Strategies
Abstract
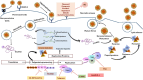
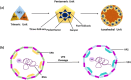
Enterovirus-D68 (EV-D68) was first identified in 1962 in pediatric patients with acute respiratory conditions in California, USA (US). From the 1970s to 2005, EV-D68 was underestimated due to limited data and serotyping methods. In 2014, the United States experienced outbreaks of acute flaccid myelitis (AFM) in children EV-D68 positive. WIN-like compounds (pleconaril, pocapavir, and vapendavir) bind to the virus capsid and have been tested against various enteroviruses (EVs) in clinical trials. However, these compounds encountered issues with resistance and adverse effects, which impeded their approval by the Food and Drug Administration (FDA). Presently, the medical field lacks FDA-approved antiviral treatments or vaccines for EV-D68. Ongoing research efforts are dedicated to identifying viable therapeutics to address EV-D68 infections. This review explores the current advancements in antiviral therapies and potential therapeutics to mitigate the significant impact of EV-D68 infection control.
Keywords: WIN‐like compounds; acute flaccid myelitis; broad‐spectrum antiviral; contemporary strains; drug‐resistance; enterovirus‐D68; type‐I interferon; viral life cycle.
© 2024 The Author(s). Influenza and Other Respiratory Viruses published by John Wiley & Sons Ltd.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Schieble J. H., Fox V. L., and Lennette E. H., “A Probable New Human Picornavirus Associated With Respiratory Diseases,” American Journal of Epidemiology 85, no. 2 (1967): 297–310. - PubMed
-
- Shi Y., Liu Y., Wu Y., Hu S., and Sun B., “Molecular Epidemiology and Recombination of Enterovirus D68 in China,” Infection, Genetics and Evolution 115 (2023): 105512. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Supplementary concepts
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

