Epiploic Appendagitis in a Young Adult Female: A Rare Cause of Acute Abdominal Pain
- PMID: 39703314
- PMCID: PMC11655675
- DOI: 10.7759/cureus.73953
Epiploic Appendagitis in a Young Adult Female: A Rare Cause of Acute Abdominal Pain
Abstract
Epiploic appendagitis (EA) is an uncommon and frequently misdiagnosed cause of acute abdominal pain, typically affecting middle-aged males. This case report presents an atypical occurrence in a 32-year-old Hispanic female who presented with left lower quadrant pain, initially suspected to be diverticulitis or infectious colitis. Contrast-enhanced CT imaging revealed the characteristic findings of EA, a diagnosis that is rarely seen in young adult females. The patient was successfully treated through conservative measures and avoided unnecessary surgical interventions. This case emphasizes the importance of considering EA in the differential diagnosis of acute abdominal pain across diverse patient demographics. It also highlights the crucial role of contrast-enhanced CT imaging to accurately diagnose and treat EA. By increasing awareness of this condition among clinicians, we can improve diagnostic accuracy, reduce unnecessary interventions, and optimize patient care in cases of acute abdominal pain.
Keywords: acute abdominal pain; conservative management; ct imaging; epiploic appendagitis; gastrointestinal disorders; inflammatory conditions; misdiagnosis; young female.
Copyright © 2024, Daly et al.
Conflict of interest statement
Human subjects: Consent for treatment and open access publication was obtained or waived by all participants in this study. Conflicts of interest: In compliance with the ICMJE uniform disclosure form, all authors declare the following: Payment/services info: All authors have declared that no financial support was received from any organization for the submitted work. Financial relationships: All authors have declared that they have no financial relationships at present or within the previous three years with any organizations that might have an interest in the submitted work. Other relationships: All authors have declared that there are no other relationships or activities that could appear to have influenced the submitted work.
Figures
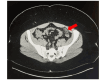
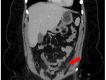
References
-
- Epiploic appendagitis: systematic review of a distinctive pathology. Acevedo-Castillo CD, Macias-Cruz HM, Ramirez-Cisneros A, Bautista-Coronado UA, Moran-Guerrero JA, Guzman EA. Am Surg. 2024;90:3074–3081. - PubMed
-
- Misdiagnosis of primary epiploic appendagitis. Rao PM, Rhea JT, Wittenberg J, Warshaw AL. Am J Surg. 1998;176:81–85. - PubMed
-
- Primary epiploic appendagitis: evolutionary changes in CT appearance. Rao PM, Wittenberg J, Lawrason JN. Radiology. 1997;204:713–717. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
