A survey of detection of Parkinson's disease using artificial intelligence models with multiple modalities and various data preprocessing techniques
- PMID: 39703622
- PMCID: PMC11657906
- DOI: 10.4103/jehp.jehp_1777_23
A survey of detection of Parkinson's disease using artificial intelligence models with multiple modalities and various data preprocessing techniques
Abstract
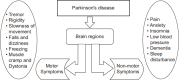
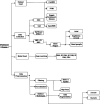
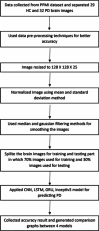
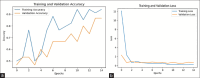
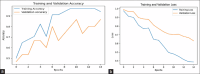
Parkinson's disease (PD) is a neurodegenerative brain disorder that causes symptoms such as tremors, sleeplessness, behavioral problems, sensory abnormalities, and impaired mobility, according to the World Health Organization (WHO). Artificial intelligence, machine learning (ML), and deep learning (DL) have been used in recent studies (2015-2023) to improve PD diagnosis by categorizing patients and healthy controls based on similar clinical presentations. This study investigates several datasets, modalities, and data preprocessing techniques from the collected data. Issues are also addressed, with suggestions for future PD research involving subgrouping and connection analysis using magnetic resonance imaging (MRI), dopamine transporter scan (DaTscan), and single-photon emission computed tomography (SPECT) data. We have used different models like Convolutional Neural Network (CNN) and Gated Recurrent Unit (GRU) for detecting PD at an early stage. We have used the Parkinson's Progression Markers Initiative (PPMI) dataset 3D brain images and archived the 86.67%, 94.02%, accuracy of models, respectively.
Keywords: Artificial intelligence; Gait; MRI; PET; Parkinson’s Disease; data preprocessing.
Copyright: © 2024 Journal of Education and Health Promotion.
Conflict of interest statement
There are no conflicts of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Spears C. Dopamine agonists retrieved. 2018. Available from: http://www.parkinson.org/understanding/parkinsons/treatment/prescription... .
-
- Armstrong MJ Okun MS. Diagnosis and treatment of Parkinson disease: A review. JAMA. 2020;323:548–60. - PubMed
-
- Valls-Solé, Josep. and Francesc Valldeoriola. “Neurophysiological correlate of clinical signs in Parkinson’s disease.”. Clinical neurophysiology. 113(6):2002, 792–805. - PubMed
-
- Brooks DJ. Imaging approaches to Parkinson disease. J Nucl Med. 2010;51:596–609. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

