Melatonin as a multifunctional modulator: emerging insights into its role in health, reproductive efficiency, and productive performance in livestock
- PMID: 39703668
- PMCID: PMC11655511
- DOI: 10.3389/fphys.2024.1501334
Melatonin as a multifunctional modulator: emerging insights into its role in health, reproductive efficiency, and productive performance in livestock
Abstract
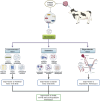
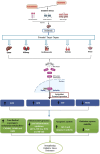
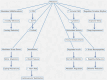
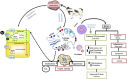
Melatonin, a pleiotropic hormone plays a vital role in enhancing livestock performance not only by regulating circadian rhythms but also by exhibiting antioxidant, immunomodulatory, and metabolic regulatory effects that collectively improve resilience, fertility, and productivity. Melatonin's synthesis is predominantly influenced by light exposure, with increased production in darkness; however, factors such as diet and health status further modulate its levels. By helping animals adapt to environmental stressors, melatonin boosts immune responses, mitigates chronic illnesses, and optimizes production efficiency. Its regulatory influence extends to the hypothalamic-pituitary-gonadal (HPG) axis, enhancing hormone secretion, synchronizing estrous cycles, and improving embryo viability. This results in improved reproductive outcomes through the protection of gametes, increased sperm motility, and enhanced oocyte quality, all of which benefit the fertilization process. Additionally, melatonin positively impacts productive performance, promoting muscle growth, development, and optimizing milk yield and composition through its interaction with metabolic and endocrine systems. As ongoing research continues to uncover its broader physiological effects, melatonin supplementation emerges as a promising approach to improving livestock welfare, productivity, and sustainability in modern animal husbandry.
Keywords: animal performance; antioxidant status; health; melatonin; production potential.
Copyright © 2024 Afzal.
Conflict of interest statement
The author declares that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Abulaiti A., Nawaz M., Naseer Z., Ahmed Z., Liu W., Abdelrahman M., et al. (2023). Administration of melatonin prior to modified synchronization protocol improves the productive and reproductive efficiency of Chinese crossbred buffaloes in low breeding season. Front. Vet. Sci. 10, 1118604. 10.3389/fvets.2023.1118604 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

