RUNX2 Phase Separation Mediates Long-Range Regulation Between Osteoporosis-Susceptibility Variant and XCR1 to Promote Osteoblast Differentiation
- PMID: 39704037
- PMCID: PMC11809430
- DOI: 10.1002/advs.202413561
RUNX2 Phase Separation Mediates Long-Range Regulation Between Osteoporosis-Susceptibility Variant and XCR1 to Promote Osteoblast Differentiation
Abstract
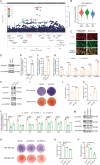
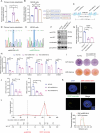
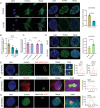
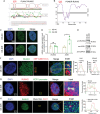
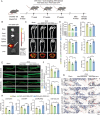
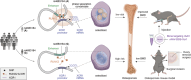
GWASs have identified many loci associated with osteoporosis, but the underlying genetic regulatory mechanisms and the potential drug target need to be explored. Here, a new regulatory mechanism is found that a GWAS intergenic SNP (rs4683184) functions as an enhancer to influence the binding affinity of transcription factor RUNX2, whose phase separation can mediate the long-range chromatin interaction between enhancer and target gene XCR1 (a member of the GPCR family), leading to changes of XCR1 expression and osteoblast differentiation. Bone-targeting AAV of Xcr1 can improve bone formation in osteoporosis mice, suggesting that XCR1 can be a new susceptibility gene for osteoporosis. This study is the first to link non-coding SNP with phase separation, providing a new insight into long-range chromatin regulation mechanisms with susceptibility to complex diseases, and finding a potential target for the development of osteoporosis drugs and corresponding translational research.
Keywords: GWAS; RUNX2; XCR1; osteoporosis; phase separation.
© 2024 The Author(s). Advanced Science published by Wiley‐VCH GmbH.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Ensrud K. E., J. Am. Med. Assoc. 2021, 325, 96.
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- 32300486/National Natural Science Foundation of China
- 82170896/National Natural Science Foundation of China
- 32170616/National Natural Science Foundation of China
- 2021JC-02/Science Fund for Distinguished Young Scholars of Shaanxi Province
- 2022TD-44/Innovation Capability Support Program of Shaanxi Province
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
