Changes in iPSC-astrocyte morphology reflect Alzheimer's disease patient clinical markers
- PMID: 39704342
- PMCID: PMC11907432
- DOI: 10.1093/stmcls/sxae085
Changes in iPSC-astrocyte morphology reflect Alzheimer's disease patient clinical markers
Abstract
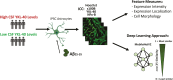
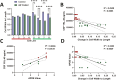
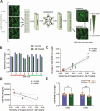
Human induced pluripotent stem cells (iPSCs) provide powerful cellular models of Alzheimer's disease (AD) and offer many advantages over non-human models, including the potential to reflect variation in individual-specific pathophysiology and clinical symptoms. Previous studies have demonstrated that iPSC-neurons from individuals with Alzheimer's disease (AD) reflect clinical markers, including β-amyloid (Aβ) levels and synaptic vulnerability. However, despite neuronal loss being a key hallmark of AD pathology, many risk genes are predominantly expressed in glia, highlighting them as potential therapeutic targets. In this work iPSC-derived astrocytes were generated from a cohort of individuals with high versus low levels of the inflammatory marker YKL-40, in their cerebrospinal fluid (CSF). iPSC-derived astrocytes were treated with exogenous Aβ oligomers and high content imaging demonstrated a correlation between astrocytes that underwent the greatest morphology change from patients with low levels of CSF-YKL-40 and more protective APOE genotypes. This finding was subsequently verified using similarity learning as an unbiased approach. This study shows that iPSC-derived astrocytes from AD patients reflect key aspects of the pathophysiological phenotype of those same patients, thereby offering a novel means of modelling AD, stratifying AD patients and conducting therapeutic screens.
Keywords: YKL-40; astrocyte; deep learning; morphology; stem cell.
© The Author(s) 2024. Published by Oxford University Press.
Conflict of interest statement
H.Z. has served at scientific advisory boards and/or as a consultant for Abbvie, Acumen, Alector, Alzinova, ALZPath, Annexon, Apellis, Artery Therapeutics, AZTherapies, CogRx, Denali, Eisai, Nervgen, Novo Nordisk, Optoceutics, Passage Bio, Pinteon Therapeutics, Prothena, Red Abbey Labs, reMYND, Roche, Samumed, Siemens Healthineers, Triplet Therapeutics, and Wave, has given lectures in symposia sponsored by Cellectricon, Fujirebio, Alzecure, Biogen, and Roche, and is a co-founder of Brain Biomarker Solutions in Gothenburg AB (BBS), which is a part of the GU Ventures Incubator Program (outside submitted work). MZC is Director of Oxford StemTech Ltd and Human-Centric DD Ltd. The other authors report no conflict of interests
Figures

Comment in
-
Comment on "Changes in iPSC-Astrocyte Morphology Reflect Alzheimer's Disease Patient Clinical Markers".Stem Cells. 2025 Jun 24;43(7):sxaf030. doi: 10.1093/stmcls/sxaf030. Stem Cells. 2025. PMID: 40355984 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
In reply to Letter to the Editor from Paudel: Comment on "Changes in iPSC-Astrocyte Morphology Reflect Alzheimer's Disease Patient Clinical Markers".Stem Cells. 2025 Jun 24;43(7):sxaf031. doi: 10.1093/stmcls/sxaf031. Stem Cells. 2025. PMID: 40371929 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
-
- Israel MA, Yuan SH, Bardy C, et al. Probing sporadic and familial Alzheimer’s disease using induced pluripotent stem cells. Nature. 2012;482:216-220. https://doi.org/ 10.1038/nature10821 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Kondo T, Asai M, Tsukita K, et al. Modeling Alzheimer’s disease with iPSCs reveals stress phenotypes associated with intracellular Abeta and differential drug responsiveness. Cell Stem Cell. 2013;12:487-496. https://doi.org/ 10.1016/j.stem.2013.01.009 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Lagomarsino VN, Pearse RV, Liu L, et al. Stem cell-derived neurons reflect features of protein networks, neuropathology, and cognitive outcome of their aged human donors. Neuron. 2021;109:3402-3420.e9. https://doi.org/ 10.1016/j.neuron.2021.08.003 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Ng B, Rowland HA, Wei T, et al. Neurons derived from individual early Alzheimer’s disease patients reflect their clinical vulnerability. Brain Commun. 2022;4:fcac267. https://doi.org/ 10.1093/braincomms/fcac267 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Shen LX, Jia JP.. An overview of genome-wide association studies in Alzheimer’s disease. Neurosci Bull. 2016;32:183-190. https://doi.org/ 10.1007/s12264-016-0011-3 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- MR/N029941/1/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- MC_EX_MR/N50192X/1/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- MR/L023784/2/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- MR/M024962/1/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- MR/M024962/1/Medical Research Council Dementias Platform UK Experimental Medicine Award
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

