Identification of α-galactosylceramide as an endogenous mammalian antigen for iNKT cells
- PMID: 39704712
- PMCID: PMC11660903
- DOI: 10.1084/jem.20240728
Identification of α-galactosylceramide as an endogenous mammalian antigen for iNKT cells
Abstract
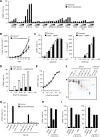
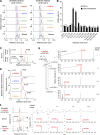
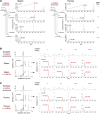
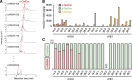
Invariant natural killer T (iNKT) cells are unconventional T cells recognizing lipid antigens in a CD1d-restricted manner. Among these lipid antigens, α-galactosylceramide (α-GalCer), which was originally identified in marine sponges, is the most potent antigen. Although the presence of α-anomeric hexosylceramide and microbiota-derived branched α-GalCer is reported, antigenic α-GalCer has not been identified in mammals. Here, we developed a high-resolution separation and detection system, supercritical fluid chromatography tandem mass spectrometry (SFC/MS/MS), that can discriminate hexosylceramide diastereomers (α-GalCer, α-GlcCer, β-GalCer, or β-GlcCer). The B16 melanoma tumor cell line does not activate iNKT cells; however, ectopic expression of CD1d was sufficient to activate iNKT cells without adding antigens. B16 melanoma was unlikely to generate iNKT cell antigens; instead, antigen activity was detected in cell culture serum. Activity-based purification and SFC/MS/MS identified dihydrosphingosine-based saturated α-GalCer as an antigenic component in serum, bile, and lymphoid tissues. These results show the first evidence for the presence of potent antigenic α-GalCer in mammals.
© 2024 Hosono et al.
Conflict of interest statement
Disclosures: The authors declare no competing interests exist.
Figures




References
-
- Brennan, P.J., Tatituri R.V.V., Heiss C., Watts G.F.M., Hsu F.F., Veerapen N., Cox L.R., Azadi P., Besra G.S., and Brenner M.B.. 2014. Activation of iNKT cells by a distinct constituent of the endogenous glucosylceramide fraction. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA. 111:13433–13438. 10.1073/pnas.1415357111 - DOI - PMC - PubMed

