NK cells restrain cytotoxic CD8+ T cells in the submandibular gland via PD-1-PD-L1
- PMID: 39705335
- PMCID: PMC12099074
- DOI: 10.1126/sciimmunol.adl2967
NK cells restrain cytotoxic CD8+ T cells in the submandibular gland via PD-1-PD-L1
Abstract
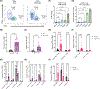
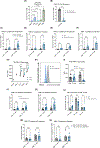
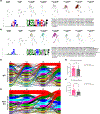
The increasing use of anti-programmed cell death 1 (PD-1) immune checkpoint blockade has led to the emergence of immune-related adverse events (irAEs), including dysfunction of the submandibular gland (SMG). In this study, we investigated the immunoregulatory mechanism contributing to the susceptibility of the SMG to irAEs. We found that the SMGs of PD-1-deficient mice and anti-programmed cell death ligand 1 (PD-L1)-treated mice harbor an expanded population of CD8+ T cells. We demonstrate that natural killer (NK) cells expressing PD-L1 tightly regulate CD8+ T cells in the SMG. When this immunoregulation is disrupted, CD8+ T cells clonally expand and acquire a unique transcriptional profile consistent with T cell receptor (TCR) activation. These clonally expanded cells phenotypically overlapped with cytotoxic GzmK+ CD8+ T autoimmune cells identified in patients with primary Sjögren's syndrome. Understanding how NK cells modulate CD8+ T cell activity in the SMG opens new avenues for preventing irAEs in patients undergoing checkpoint blockade therapies.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures


References
-
- Chaudhry MZ, Belz GT, Chameleon impersonation of NK cells and ILC1s. Nat Immunol 25, 1313–1315 (2024). - PubMed
-
- Cortez VS, Fuchs A, Cella M, Gilfillan S, Colonna M, Cutting Edge: Salivary Gland NK Cells Develop Independently of Nfil3 in Steady-State. The Journal of Immunology 192, 4487–4491 (2014). - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

