TNIK: A redox sensor in endothelial cell permeability
- PMID: 39705357
- PMCID: PMC11661440
- DOI: 10.1126/sciadv.adk6583
TNIK: A redox sensor in endothelial cell permeability
Abstract
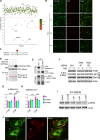
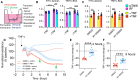
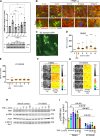
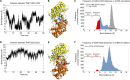
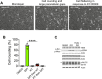
Dysregulation of endothelial barrier integrity can lead to vascular leak and potentially fatal oedema. TNF-α controls endothelial permeability during inflammation and requires the actin organizing Ezrin-Radixin-Moesin (ERM) proteins. We identified TRAF2 and NCK-interacting kinase (TNIK) as a kinase directly phosphorylating and activating ERM, specifically at the plasma membrane of primary human endothelial cells. TNIK mediates TNF-α-dependent cellular stiffness and paracellular gap formation in vitro and is essential in driving inflammatory oedema formation in vivo. Unlike its homologs, TNIK activity is negatively and reversibly regulated by H2O2-mediated oxidation of C202 within the kinase domain. TNIK oxidation results in intermolecular disulfide bond formation and loss of kinase activity. Pharmacologic inhibition of endogenous reactive oxygen species production in endothelial cells elevated TNIK-dependent ERM phosphorylation, endothelial cell contraction, and cell rounding. Together, we highlight an interplay between TNIK, ERM phosphorylation, and redox signalling in regulating TNF-induced endothelial cell permeability.
Figures


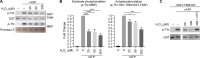
References
-
- Komarova Y., Malik A. B., Regulation of endothelial permeability via paracellular and transcellular transport pathways. Annu. Rev. Physiol. 72, 463–493 (2010). - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

