Real-World Outcomes in Patients With Metastatic Renal Cell Carcinoma Treated With First-Line Nivolumab Plus Ipilimumab in the United States
- PMID: 39705641
- PMCID: PMC11670916
- DOI: 10.1200/CCI.24.00132
Real-World Outcomes in Patients With Metastatic Renal Cell Carcinoma Treated With First-Line Nivolumab Plus Ipilimumab in the United States
Erratum in
-
Erratum: Real-World Outcomes in Patients With Metastatic Renal Cell Carcinoma Treated With First-Line Nivolumab Plus Ipilimumab in the United States.JCO Clin Cancer Inform. 2025 Mar;9:e2500026. doi: 10.1200/CCI-25-00026. Epub 2025 Mar 5. JCO Clin Cancer Inform. 2025. PMID: 40042262 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Abstract
Purpose: Nivolumab plus ipilimumab (NIVO + IPI) is a first-in-class combination immunotherapy for the treatment of intermediate- or poor (I/P)-risk advanced or metastatic renal cell carcinoma (mRCC). Currently, there are limited real-world data regarding clinical effectiveness beyond 12-24 months from treatment initiation. In this real-world study, treatment patterns and clinical outcomes were evaluated for NIVO + IPI in a community oncology setting.
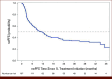
Methods: A retrospective analysis using electronic medical record data from The US Oncology Network examined patients with I/P-risk clear cell mRCC who initiated first-line (1L) NIVO + IPI between January 4, 2018, and December 31, 2019, with follow-up until June 30, 2022. Baseline demographics, clinical characteristics, treatment patterns, clinical effectiveness, and safety outcomes were assessed descriptively. Overall survival (OS) and real-world progression-free survival (rwPFS) were analyzed using Kaplan-Meier methods.
Results: Among 187 patients identified (median follow-up, 22.4 months), with median age 63 (range, 30-89) years, 74 (39.6%) patients had poor risk and 37 (19.8%) patients had Eastern Cooperative Oncology Group performance status score ≥2. Of 86 patients who received second-line therapy, 54.7% received cabozantinib and 10.5% received pazopanib. The median (95% CI) OS and rwPFS were 38.4 (24.7-46.1) months and 11.1 (7.5-15.0) months, respectively. Treatment-related adverse events (TRAEs) were reported in 89 (47.6%) patients, including fatigue (n = 25, 13.4%) and rash (n = 19, 10.2%).
Conclusion: This study provides data to support the understanding of the real-world utilization and long-term effectiveness of 1L NIVO + IPI in patients with I/P-risk mRCC. TRAE rates were low relative to clinical trials.
Conflict of interest statement
The following represents disclosure information provided by authors of this manuscript. All relationships are considered compensated unless otherwise noted. Relationships are self-held unless noted. I = Immediate Family Member, Inst = My Institution. Relationships may not relate to the subject matter of this manuscript. For more information about ASCO's conflict of interest policy, please refer to
Open Payments is a public database containing information reported by companies about payments made to US-licensed physicians (
No other potential conflicts of interest were reported.
Figures



References
-
- National Cancer Institute : Surveillance, Epidemiology, and End Results Program: Cancer Stat Facts, Kidney and Renal Pelvis, 2023. https://seer.cancer.gov/statfacts/html/kidrp.html
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

