Nuclear microRNA 9 mediates G-quadruplex formation and 3D genome organization during TGF-β-induced transcription
- PMID: 39706840
- PMCID: PMC11662019
- DOI: 10.1038/s41467-024-54740-x
Nuclear microRNA 9 mediates G-quadruplex formation and 3D genome organization during TGF-β-induced transcription
Abstract
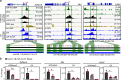
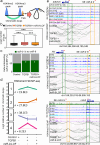
The dynamics of three-dimensional (3D) genome organization are essential to transcriptional regulation. While enhancers regulate spatiotemporal gene expression, chromatin looping is a means for enhancer-promoter interactions yielding cell-type-specific gene expression. Further, non-canonical DNA secondary structures, such as G-quadruplexes (G4s), are related to increased gene expression. However, the role of G4s in promoter-distal regulatory elements, such as super-enhancers (SE), and in chromatin looping has remained elusive. Here we show that mature microRNA 9 (miR-9) is enriched at promoters and SE of genes that are inducible by transforming growth factor beta 1 (TGFB1) signaling. Moreover, we find that miR-9 is required for formation of G4s, promoter-super-enhancer looping and broad domains of the euchromatin histone mark H3K4me3 at TGFB1-responsive genes. Our study places miR-9 in the same functional context with G4s and promoter-enhancer interactions during 3D genome organization and transcriptional activation induced by TGFB1 signaling, a critical signaling pathway in cancer and fibrosis.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests: The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures







References
-
- Jerkovic, I. & Cavalli, G. Understanding 3D genome organization by multidisciplinary methods. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol.22, 511–528 (2021). - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

