CircIRAK3 Promotes Neutrophil Extracellular Trap Formation by Improving the Stability of ELANE mRNA in Sepsis
- PMID: 39707013
- PMCID: PMC12336077
- DOI: 10.1007/s10753-024-02206-z
CircIRAK3 Promotes Neutrophil Extracellular Trap Formation by Improving the Stability of ELANE mRNA in Sepsis
Abstract
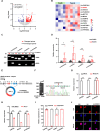
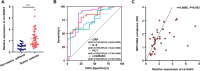
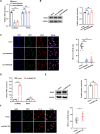
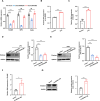
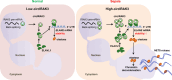
Excessive formation of neutrophil extracellular traps (NETs) has been shown to exacerbate inflammatory injury and organ damage in patients with sepsis. Circular RNAs (circRNAs) abnormally expressed in immune cells of sepsis patients, and play an important role in the pathogenesis of dysregulated immune responses. However, the functions of circRNAs in NET formation during sepsis remain unknown. Here, we identified circIRAK3, a novel circRNA that was upregulated in peripheral blood neutrophils of sepsis patients. Combining clinical data, we revealed that elevated circIRAK3 was positively correlated with blood NET levels. Furthermore, knockdown and overexpression in differentiated HL-60 (dHL-60) neutrophil-like cells demonstrated that circIRAK3 promoted NET formation. In addition, we found that circIRAK3 promoted NET formation via positively regulating elastase expression in dHL-60 cells when treated with inflammatory stimuli. Mechanistically, circIRAK3 directly interacted with ELAVL1 to improve ELANE mRNA stability and consequently promote elastase protein expression. In summary, our study reveals that circIRAK3 promotes NET formation in sepsis by increasing ELANE mRNA levels.
Keywords: Circular RNA; ELANE; ELAVL1; Neutrophil extracellular trap; Sepsis; mRNA stability.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Declarations. Ethics: The present study was approved by the Ethics Committee at Daping Hospital of Army Medical University (No. 66, 2020). All study participants provided written informed consent. Conflict of Interest: The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
References
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

