Elongation factor 2 in cancer: a promising therapeutic target in protein translation
- PMID: 39707196
- PMCID: PMC11660736
- DOI: 10.1186/s11658-024-00674-7
Elongation factor 2 in cancer: a promising therapeutic target in protein translation
Abstract
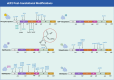
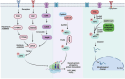
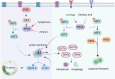
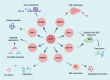
Aberrant elongation of proteins can lead to the activation of oncogenic signaling pathways, resulting in the dysregulation of oncogenic signaling pathways. Eukaryotic elongation factor 2 (eEF2) is an essential regulator of protein synthesis that precisely elongates nascent peptides in the protein elongation process. Although studies have linked aberrant eEF2 expression to various cancers, research has primarily focused on its structure, highlighting a need for deeper exploration into its molecular functions. In this review, recent advancements in the structure, guanosine triphosphatase (GTPase) activity, posttranslational modifications, regulatory factors, and inhibitors of eEF2 are summarized. These findings provide a comprehensive cognition on the critical role of eEF2 and its potential as a therapeutic target in cancer. Furthermore, this review highlights important unanswered questions that warrant investigation in future research.
Keywords: Cancer; Elongation factor 2; Inhibitors; Protein elongation; Regulators.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Declarations. Ethics approval and consent to participate: Not applicable. Consent for publication: Not applicable. Competing interests: The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures

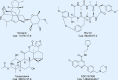
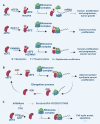
References
-
- Rodnina MV. Decoding and recoding of mRNA sequences by the ribosome. Annu Rev Biophys. 2023;52:161–82. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

