Phosphoinositide signaling in the nucleus: Impacts on chromatin and transcription regulation
- PMID: 39707648
- PMCID: PMC11771838
- DOI: 10.1111/boc.202400096
Phosphoinositide signaling in the nucleus: Impacts on chromatin and transcription regulation
Abstract
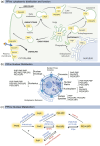
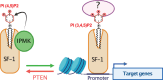
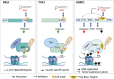
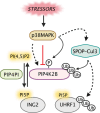
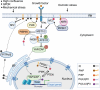
Phosphoinositides also called Polyphosphoinositides (PPIns) are small lipid messengers with established key roles in organelle trafficking and cell signaling in response to physiological and environmental inputs. Besides their well-described functions in the cytoplasm, accumulating evidences pointed to PPIns involvement in transcription and chromatin regulation. Through the description of previous and recent advances of PPIns implication in transcription, this review highlights key discoveries on how PPIns modulate nuclear factors activity and might impact chromatin to modify gene expression. Finally, we discuss how PPIns nuclear and cytosolic metabolisms work jointly in orchestrating key transduction cascades that end in the nucleus to modulate gene expression.
© 2024 The Author(s). Biology of the Cell published by Wiley‐VCH GmbH on behalf of Société Française des Microscopies and Société de Biologie Cellulaire de France.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Andjelkovic, M. , Alessi, D.R. , Meier, R. , Fernandez, A. , Lamb, N.J.C. , Frech, M. , Cron, P. , Cohen, P. , Lucocq, J.M. & Hemmings, B.A. (1997) Role of translocation in the activation and function of protein kinase B. Journal of Biological Chemistry, 272, 31515–31524. Available from: 10.1074/jbc.272.50.31515 - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

