Emerging clinical evidence of a dual role for Ang-2 and VEGF-A blockade with faricimab in retinal diseases
- PMID: 39708087
- PMCID: PMC12148975
- DOI: 10.1007/s00417-024-06695-4
Emerging clinical evidence of a dual role for Ang-2 and VEGF-A blockade with faricimab in retinal diseases
Abstract
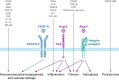
Anti-vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) therapies have transformed the treatment of retinal diseases. However, VEGF signaling is only one component of the complex, multifactorial pathophysiology of retinal diseases, and many patients have residual disease activity despite ongoing anti-VEGF treatment. The angiopoietin/tyrosine kinase with immunoglobulin and epidermal growth factor receptor-2 (Ang/Tie2) signaling pathway is critical to endothelial cell homeostasis, survival, integrity, and vascular stability. Ang-2 can interfere with Ang-1/Tie2 signaling and is increased in several retinal diseases. Lack of Tie2 signaling due to elevated Ang-2 levels drives vascular instability through pericyte dropout, neovascularization, vascular leakage, inflammation, and fibrosis. Although Ang-2 and VEGF can synergistically promote vascular instability and neovascularization, Ang-2 may also mediate vascular instability independently of VEGF. Faricimab is a bispecific antibody designed for intraocular use that inhibits two distinct pathways via Ang-2 and VEGF-A blockade. Clinical biomarkers of vascular instability are important for evaluating disease control and subsequent treatment decisions. These biomarkers include measurement/evaluation with optical coherence tomography (OCT) of intraretinal fluid, subretinal fluid, central subfield thickness, and pigment epithelial detachments (PEDs), and fluorescein angiography imaging of macular leakage and PEDs. Hyperreflective foci (HRF), thought to be representative of activated microglia, indicating an inflammatory microenvironment, and epiretinal membranes (ERMs), a marker for retinal fibrotic proliferation in diabetic macular edema (DME), are both also identified using OCT. Here we summarize data (secondary endpoint and prespecified exploratory analyses as well as post hoc analyses) from six Phase III trials suggest that dual therapy Ang-2/VEGF-A inhibition with faricimab (6 mg) has a greater effect on reducing/resolving biomarkers of vascular instability than aflibercept (2 mg), by both controlling neovascularization and vascular leakage (with resultant resolution of exudation associated with DME, neovascular age-related macular degeneration, and retinal vein occlusion), as well as by targeting inflammation (reduction of HRF in DME) and retinal fibrotic proliferation (reducing the risk of ERMs in eyes with DME). Modulation of both the Ang-2 and VEGF-A pathways with faricimab may therefore provide greater disease control than anti-VEGF monotherapy, potentially leading to extended treatment durability and improved long-term outcomes.
Keywords: Ang-2; Diabetic macular edema; Diabetic retinopathy; Neovascular age-related macular degeneration; Retinal vein occlusion; VEGF-A.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Declarations. Ethical approval: This article does not contain any studies with human participants or animals performed by any of the authors. Conflicts of interest: Varun Chaudhary has received advisory board fees from Alcon, Roche, Bayer, Novartis, Appelis, Boehringer Ingelheim, and grants from Bayer, Novartis, Roche. Florie Mar and Manuel J. Amador are employees of Genentech, Inc., and own stocks/shares with Genentech, Inc./F. Hoffmann-La Roche Ltd. Andrew Chang has received consulting role fees from Novartis, Bayer, Allergan, Roche, Alcon, Apellis, Zeiss, Astellas Pharma, Opthea, and research grants from Roche, Bayer, Novartis. Kara Gibson, Philippe Margaron, and Insaf Saffar are employed by F. Hoffmann-La Roche Ltd and own stocks/shares with F. Hoffmann-La Roche Ltd. Antonia M. Joussen has received consulting role fees from Novartis, Roche, Bayer, Genentech, Inc., AbbVie, Boehringer Ingelheim, and grants from Novartis, Roche, Bayer, Genentech, Inc., AbbVie, Boehringer Ingelheim, Johnson & Johnson. Judy E. Kim has received advisory board fees from AbbVie, Alimera Sciences, Amgen, Apellis, Bausch & Lomb, Clearside Biomedical, Dutch Ophthalmic Research Center, Eyepoint, Genentech/Roche, Neurotech, Notal Vision, Ophthalmic Therapeutics, Regeneron. Junyeop Lee has received consulting role fees from AbbVie/Allergan, AMC sciences, Bayer, Curacle, Novartis, Roche; and grants/research support from Bayer, Novartis. David Wong has received grants/research support from Bayer, Novartis, Roche, and consulting role fees from AbbVie/Allergan, Alcon, Apellis, Bausch Health, Biogen, Boehringer Ingelheim, Bayer, Novartis, Ripple Therapeutics, Roche, Topcon, Zeiss. Charles Wykoff has received consulting fees/honoraria for ongoing services for 4DMT, AbbVie, Adverum, Aerie, AGTC, Alcon, Alimera, Alkeus, Allgenesis, Alnylam, AMC Sciences, Annexon, Apellis, Arrowhead, Ascidian, Aviceda, Bausch + Lomb, Bayer, Biocryst, Bionic Vision, Boehringer Ingelheim, Cholgene, Clearside, Curacle, Emmecell, EyeBiotech, EyePoint, Foresite, Frontera, Genentech, Gyroscope, IACTA, InGel, IVERIC Bio, Janssen, Kato, Kiora, Kodiak, Kriya, Merck, Merit, Nanoscope, Neurotech, NGM, Notal Vision, Novartis, OccuRx, Ocular Therapeutix, Ocuphire, Ocuterra, OliX, ONL, Opthea, Osanni, Oxular, Palatin, Perceive Bio, Perfuse, Ray, RecensMedical, Regeneron, RegenXBio, Resonance, Roche, Sandoz, Sanofi, Santen, SciNeuro, Stealth, Surrozen, Suzhou Raymon, Sylentis, THEA, Therini, TissueGen, Valo, Verana, Visgenx, Zeiss, grants paid to institution for ongoing research support as a Principal Investigator for trials sponsored by 4DMT, Adverum, AffaMed, Alexion, Alimera, Alkahest, Allgenesis, Amgen, Annexin, Annexon, Apellis, Ascidian, Asclepix, Aviceda, Bayer, Boehringer Ingelheim, Chengdu Kanghong, Chengdu Origen, Clearside, Curacle, EyeBiotech, EyePoint, Gemini, Genentech, GlaxoSmithKline, Gyroscope, IONIS, iRENIX, IVERIC bio, Janssen, Kodiak, Kyoto DDD, Kyowa Kirin, Nanoscope, Neurotech, NGM, Novartis, Ocugen, Ocular Therapeutix, Ocuphire, OcuTerra, OliX, Opthea, Outlook Therapeutics, Oxular, Oxurion, Oyster Point, Perceive Bio, Pykus, RecensMedical, Regeneron, RegenXBio, Rezolute, Roche, SamChunDang Pharm, Sandoz, Shanghai Henlius, Skyline, Stealth, UNITY, Valo, Verily, Xbrane, and stock options (not owner) ongoing from private for-profit entities: InGel, ONL, Osanni, Panther, PolyPhotonix, RecensMedical, TissueGen, Visgenx, Vitranu. Srinivas Sadda has received consulting role fees from Roche/Genentech, Apellis, Amgen, AbbVie/Allergan, Alexion, Samsung Bioepis, Biogen, Boehringer Ingelheim, Iveric Bio, Novartis, Bayer, Pfizer, Astellas, Nanoscope, Jannsen, CenterVue, Optos, Heidelberg, Notal Vision, Topcon, Eyepoint, Character, Ocular Therapeutics, Neurotech, and honoraria/speaker fees from Novartis, Roche, Optos, Heidelberg, NIDEK, is a member of data safety monitoring boards for Regeneron, Regenxbio, and received Research Instruments from iCare, Carl Zeiss Meditec, Optos, NIDEK, Topcon, Heidelberg. Dr Srinivas Sadda and Dr Antonia Joussen are co-editors-in-chief of Graefe's Archive for Clinical and Experimental Ophthalmology.
Figures
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

