Three-year Seroprevalence of SARS-CoV-2 Nucleocapsid Protein Antibody Among Children, Parental Awareness, and Contributors of Infection: A Single-school Cohort Study in Chiba, Japan
- PMID: 39710421
- PMCID: PMC12066190
- DOI: 10.2188/jea.JE20240284
Three-year Seroprevalence of SARS-CoV-2 Nucleocapsid Protein Antibody Among Children, Parental Awareness, and Contributors of Infection: A Single-school Cohort Study in Chiba, Japan
Abstract
Background: Coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) in children is often asymptomatic, posing challenges in detecting infections. Additionally, factors contributing to infection remain poorly understood. This study aimed to investigate trends in anti-severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) nucleocapsid antibody seroprevalence, the relationship between seroprevalence and parental perception of child infection, and factors related to COVID-19 in children.
Methods: In December 2020, 355 children aged 6-12 years in one elementary school were enrolled in the study. The anti-SARS-CoV-2 nucleocapsid antibody seroprevalence was assessed, and questionnaires were administered annually for 3 years. Parents' perceptions of infection and factors contributing to infection were examined.
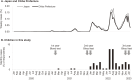
Results: The seroprevalence was 0.6%, 2.2%, and 60.9% in the first, second, and third years, respectively. The third-year seroprevalence among children reported as 'infected,' 'not tested but had symptoms,' and 'not infected' by parents was 97.3%, 83.3%, and 35.7%, respectively. Increased odds of seropositivity at the third-year measurement were observed in lower grades (adjusted odds ratio [aOR] 2.79 compared with higher grades) and in children more likely to play with others (aOR 3.97 for 'somewhat' and aOR 2.84 for 'often,' compared with 'rarely'). No significant associations with seropositivity were found for sex, siblings, body mass index, serum 25-OH vitamin D3 concentration, or sleep duration.
Conclusion: The Omicron variant outbreak from the end of 2021 led to a sharp increase in seroprevalence among children, with many unaware of their infection. Frequent play with others may facilitate transmission in children. These data provide useful information for developing countermeasures against COVID-19 and other future pandemics.
Keywords: SARS-CoV-2; awareness; child’s infection; contributing factor; seroprevalence.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflicts of interest: None declared.
Figures

Similar articles
-
SARS-CoV-2 Antibody Testing in Health Care Workers: A Comparison of the Clinical Performance of Three Commercially Available Antibody Assays.Microbiol Spectr. 2021 Oct 31;9(2):e0039121. doi: 10.1128/Spectrum.00391-21. Epub 2021 Sep 29. Microbiol Spectr. 2021. PMID: 34585976 Free PMC article.
-
Seroprevalence Trends of Antibodies to SARS-CoV-2 in South Korea, 2021-2022: A Repeated Cross-Sectional Study.Influenza Other Respir Viruses. 2025 Jun;19(6):e70117. doi: 10.1111/irv.70117. Influenza Other Respir Viruses. 2025. PMID: 40462400 Free PMC article.
-
The seroprevalence of SARS-CoV-2-specific antibodies in Australian children: A cross-sectional study.PLoS One. 2024 Sep 18;19(9):e0300555. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0300555. eCollection 2024. PLoS One. 2024. PMID: 39292730 Free PMC article.
-
Population-based seroprevalence surveys of anti-SARS-CoV-2 antibody: An up-to-date review.Int J Infect Dis. 2020 Dec;101:314-322. doi: 10.1016/j.ijid.2020.10.011. Epub 2020 Oct 9. Int J Infect Dis. 2020. PMID: 33045429 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Seroprevalence of SARS-CoV-2-specific antibodies in cancer outpatients in Madrid (Spain): A single center, prospective, cohort study and a review of available data.Cancer Treat Rev. 2020 Nov;90:102102. doi: 10.1016/j.ctrv.2020.102102. Epub 2020 Sep 1. Cancer Treat Rev. 2020. PMID: 32947121 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- WHO. Origin of SARS-CoV-2. https://iris.who.int/bitstream/handle/10665/332197/WHO-2019-nCoV-FAQ-Vir...; 2020 Accessed 06.03.2024.
-
- WHO. COVID-19 dashboard. https://data.who.int/dashboards/covid19/cases?n=c; 2024 Accessed 06.03.2024.
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

