Treatment of lumbar spondylolysis in young adults using modified intravertebral screw-rod fixation system for single vertebral body combined with autologous cancellous bone graft: a technical note and preliminary report
- PMID: 39710685
- PMCID: PMC11664932
- DOI: 10.1186/s13018-024-05382-8
Treatment of lumbar spondylolysis in young adults using modified intravertebral screw-rod fixation system for single vertebral body combined with autologous cancellous bone graft: a technical note and preliminary report
Abstract
Background: There is currently no consensus on the surgical treatment of lumbar spondylolysis in young adults, and the nonunion rate remains relatively high even after surgery. Therefore, in this study, we proposed a modified intravertebral screw-rod fixation technique within a single vertebral segment and investigated the clinical efficacy of this modified fixation system combined with autologous cancellous bone grafting in the treatment of lumbar spondylolysis in young adults.
Methods: This study included 28 young adults with lumbar spondylolysis who were treated at our center between 2021 and 2023. All patients underwent modified intravertebral screw-rod fixation within a single vertebral segment combined with autologous cancellous bone grafting. We performed postoperative follow-ups regularly to assess the patient's pain status using the visual analog scale (VAS), Oswestry Disability Index (ODI), and radiological findings.
Results: All 28 patients successfully underwent the surgery with an average operation time and blood loss volume of 96.01 ± 21.3 min and 186.78 ± 63.43 mL, respectively. Postoperatively, patients experienced significant symptom relief, with notable decreases in VAS scores and ODI indices at 1, 3, 6, and 12 months compared with preoperative conditions. These differences were statistically significant (P < 0.05). Radiological findings revealed a healing rate of 92.86% for the 56 fractured pars interarticularis among the 28 patients. No implant-related complications, such as fracture, loosening, or pseudarthrosis, were observed.
Conclusions: The modified intravertebral screw-rod fixation system within a single vertebral segment combined with autologous cancellous bone grafting is a safe and effective treatment for lumbar spondylolysis in young adults. It significantly improves pain and functional disability as it promotes bone healing.
Keywords: Bone healing; Clinical outcome; Internal fixation; Lumbar spondylolysis; Young adults.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Declarations. Ethics approval and consent to participate: This study was approved by the Biomedical Ethics Committee of the 900th Hospital of the Joint Logistics Support Force (Ethics Batch No. 2021-061). Informed consent was obtained from all the participants (or their guardians) included in the study. Consent for publication: The patient described in the “Illustrative case” provided informed consent for the publication of the report and accompanying images. Competing interests: The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures


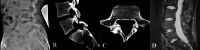
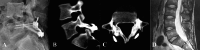
References
-
- Wang JP, Zhong ZC, Cheng CK, Chen CS, Yu CH, Chang TK, et al. Finite element analysis of the spondylolysis in lumbar spine. Biomed Mater Eng. 2006;16:301–8. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

