Discovery of MDI-114215: A Potent and Selective LIMK Inhibitor To Treat Fragile X Syndrome
- PMID: 39711116
- PMCID: PMC11726654
- DOI: 10.1021/acs.jmedchem.4c02694
Discovery of MDI-114215: A Potent and Selective LIMK Inhibitor To Treat Fragile X Syndrome
Abstract
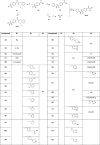
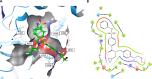
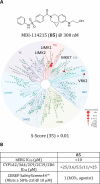
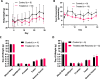
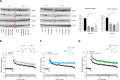
LIMKs are serine/threonine and tyrosine kinases responsible for controlling cytoskeletal dynamics as key regulators of actin stability, ensuring synaptic health through normal synaptic bouton structure and function. However, LIMK1 overactivation results in abnormal dendritic synaptic development that characterizes the pathogenesis of Fragile X Syndrome (FXS). As a result, the development of LIMK inhibitors represents an emerging disease-modifying therapeutic approach for FXS. We report the discovery of MDI-114215 (85), a novel, potent allosteric dual-LIMK1/2 inhibitor that demonstrates exquisite kinome selectivity. 85 reduces phospho-cofilin in mouse brain slices and rescues impaired hippocampal long-term potentiation in brain slices from FXS mice. We also show that LIMK inhibitors are effective in reducing phospho-cofilin levels in iPSC neurons derived from FXS patients, demonstrating 85 to be a potential therapeutic candidate for FXS that could have broad application to neurological disorders or cancers caused by LIMK1/2 overactivation and actin instability.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing financial interest.
Figures
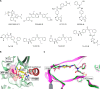
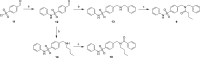




References
-
- Kashima R.; Roy S.; Ascano M.; Martinez-Cerdeno V.; Ariza-Torres J.; Kim S.; Louie J.; Lu Y.; Leyton P.; Bloch K. D.; et al. Augmented noncanonical BMP type II receptor signaling mediates the synaptic abnormality of fragile X syndrome. Sci. Signal 2016, 9 (431), ra58.10.1126/scisignal.aaf6060. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Santini E.; Huynh T. N.; Longo F.; Koo S. Y.; Mojica E.; D’Andrea L.; Bagni C.; Klann E. Reducing eIF4E-eIF4G interactions restores the balance between protein synthesis and actin dynamics in fragile X syndrome model mice. Sci. Signal 2017, 10 (504), eaan066510.1126/scisignal.aan0665. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

