Inhibition of USP22 by miR-200b-5p represses gastric cancer cell proliferation and migration by targeting the NF-κB signaling pathway
- PMID: 39711149
- PMCID: PMC12247128
- DOI: 10.3724/abbs.2024231
Inhibition of USP22 by miR-200b-5p represses gastric cancer cell proliferation and migration by targeting the NF-κB signaling pathway
Abstract
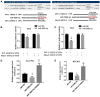
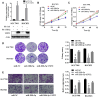
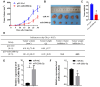
Gastric cancer (GC) is an aggressive tumor type with an intricate pathogenesis and limited therapeutic options. Ubiquitin-specific protease 22 (USP22) is a protein implicated in cell proliferation, metastasis, and tumorigenesis. However, the regulatory mechanisms governing USP22 in GC are still not fully understood. In this study, we perform bioinformatics analysis to identify conserved miRNA recognition sites for miR-200b-5p within the 3'UTR of USP22. Validation via luciferase reporter assay confirms the transcriptional regulation of USP22 by miR-200b-5p. Overexpression of miR-200b-5p markedly inhibits the proliferation and migration of GC cells in vitro and suppresses tumor growth in vivo. Conversely, ectopic expression of USP22 reversed this effect by modulating the NF-κB signaling pathway. Additionally, qPCR analysis reveals an inverse correlation between the miR-200b-5p level and USP22 expression in GC. Collectively, our findings indicate that miR-200b-5p-mediated inhibition of USP22 attenuates cell proliferation by targeting the NF-κB signaling pathway in GC, suggesting that miR-200b-5p and USP22 could serve as potential diagnostic or therapeutic targets for gastric cancer and other related human diseases.
Keywords: NF-κB; USP22; cell proliferation; gastric neoplasm; miR-200b-5p.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Figures




References
-
- Sung H, Ferlay J, Siegel RL, Laversanne M, Soerjomataram I, Jemal A, Bray F. Global cancer statistics 2020: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries. CA Cancer J Clin. . 2021;71:209–249. doi: 10.3322/caac.21660. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Chen D, Song D, Ma Y, Lu W, Qiu J, Wang Y. USP22 promotes pro-inflammatory responses in Pseudomonas aeruginosa -induced keratitis by targeting TRAF6 . Mol Med Rep. . 2022;25:149. doi: 10.3892/mmr.2022.12665. - DOI - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

