A potential inflammatory biomarker for advanced endometrial cancer treated with lenvatinib plus pembrolizumab
- PMID: 39711170
- PMCID: PMC11664300
- DOI: 10.1111/jog.16182
A potential inflammatory biomarker for advanced endometrial cancer treated with lenvatinib plus pembrolizumab
Abstract
Introduction: To identify prognostic biomarkers that could predict how well patients will respond to lenvatinib/pembrolizumab (LEN/PEM). The utility of certain inflammatory biomarkers in endometrial liquid-based cytology (LBC) or peripheral blood samples, such as neutrophil counts, lymphocyte counts, and neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio (NLR) were explored.
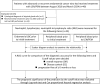
Methods: The study included 25 patients with advanced or recurrent endometrial cancer who had received LEN/PEM between August 2018 and March 2024. Predictors for overall response (OR), disease control, and progression-free survival, based on neutrophil/lymphocyte counts, NLR scores of the endometrial LBC prior to initial treatment, and peripheral blood prior to initial treatment and prior to LEM/PEM treatment were compared using a receiver operating characteristic curve. Significant predictors were evaluated using the log-rank test, and multivariate analysis.
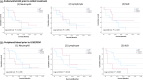
Results: Although neutrophil counts and NLR score in endometrial LBC prior to initial treatment were better effective predictors for OR, the most accurate predictor of a progression-free status was NLR score in peripheral blood prior to LEM/PEM (0.722, 95% CI: 0.45-0.99, sensitivity: 57.1%, specificity: 94.4%). In peripheral blood prior to LEN/PEM, the lower NLR (NLR <5.39) group had a significantly longer PFS than the higher NLR (5.39 ≤ NLR) group (p = 0.023, median survival: 13.5 vs. 3.0 months), and tended to be independently correlated with PFS (hazard ratio = 2.571; 95% CI = 0.857-7.719; p = 0.092).
Conclusion: Inflammatory biomarkers in endometrial LBC failed to predict the efficacy of LEN/PEM, while peripheral blood NLR score sampled prior to LEN/PEM potentially could be a significant predictor.
Keywords: endometrial cancer; lenvatinib; liquid‐based cytology; lymphocytes; neutrophil‐to‐lymphocyte ratio; pembrolizumab.
© 2024 The Author(s). Journal of Obstetrics and Gynaecology Research published by John Wiley & Sons Australia, Ltd on behalf of Japan Society of Obstetrics and Gynecology.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no conflicts of interest.
Figures


References
-
- Ott PA, Bang YJ, Berton‐Rigaud D, Elez E, Pishvaian MJ, Rugo HS, et al. Safety and antitumor activity of pembrolizumab in advanced programmed death ligand 1‐positive endometrial cancer: results from the KEYNOTE‐028 study. J Clin Oncol. 2017;35(22):2535–2541. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

