Rare but relevant: Nitrous oxide and peripheral neurotoxicity, what do we know?
- PMID: 39711181
- PMCID: PMC11986278
- DOI: 10.1111/add.16753
Rare but relevant: Nitrous oxide and peripheral neurotoxicity, what do we know?
Abstract
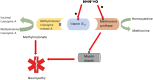
Nitrous oxide (N2O), used medically as an anaesthetic, has gained popularity as a recreational drug, with rising prevalence particularly among young adults. While its reinforcing and addictive potential remains debated, N2O is proven to be neurotoxic, especially with prolonged, heavy use, which is often unexpected for users. The neurotoxicological mechanism underlying N2O-induced neurotoxicity involves inactivation of vitamin B12 (cobalamin), which disrupts methionine synthesis, essential for maintaining the myelin sheath. This can result in demyelinating diseases, including generalized demyelinating polyneuropathy (GDP). Clinical incidence of N2O-induced peripheral neuropathy is largely unknown, although some research suggests it is not uncommon. Treatment includes immediate cessation of N2O use and vitamin B12 supplementation. Although this treatment often reverses damage, residual symptoms such as limb weakness may persist. Additionally, genetic and dietary factors, such as vitamin B12 deficiency, may heighten individual vulnerability for N2O's detrimental effects.
Keywords: methionine; myelopathy; neurotoxicity; nitrous oxide; peripheral neuropathy; vitamin B12.
© 2024 The Author(s). Addiction published by John Wiley & Sons Ltd on behalf of Society for the Study of Addiction.
Conflict of interest statement
None.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Mechanisms Involved in the Neurotoxicity and Abuse Liability of Nitrous Oxide: A Narrative Review.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Nov 25;23(23):14747. doi: 10.3390/ijms232314747. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 36499072 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Does vitamin B12 deficiency explain psychiatric symptoms in recreational nitrous oxide users? A narrative review.Clin Toxicol (Phila). 2021 Nov;59(11):947-955. doi: 10.1080/15563650.2021.1938107. Epub 2021 Aug 4. Clin Toxicol (Phila). 2021. PMID: 34348072 Review.
-
[Nitrous oxide can cause cobalamin deficiency. Vitamin B12 is a simple and cheap remedy].Lakartidningen. 1999 Nov 3;96(44):4801-5. Lakartidningen. 1999. PMID: 10584542 Review. Swedish.
-
Nitrous oxide-induced myeloneuropathy in a Thai adolescent: a case report.Paediatr Int Child Health. 2024 Aug;44(2):55-58. doi: 10.1080/20469047.2024.2344403. Epub 2024 Apr 29. Paediatr Int Child Health. 2024. PMID: 38682882
-
Neurological complications of excessive recreational nitrous oxide use: a case series based on a text mining algorithm.J Neurol. 2024 Mar;271(3):1267-1276. doi: 10.1007/s00415-023-12061-x. Epub 2023 Nov 2. J Neurol. 2024. PMID: 37914912
Cited by
-
Trends in antidote use in France from 2015 to 2021: a nationwide poison centers study.Sci Rep. 2025 Aug 18;15(1):30253. doi: 10.1038/s41598-025-15475-x. Sci Rep. 2025. PMID: 40826216 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Zacny JP, Lichtor JL, Flemming D, Coalson DW, Thompson WK. A dose‐response analysis of the subjective, psychomotor and physiological effects of intravenous morphine in healthy volunteers. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1994;268(1):1–9. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical