Diagnostic accuracy of phosphorylated tau217 in detecting Alzheimer's disease pathology among cognitively impaired and unimpaired: A systematic review and meta-analysis
- PMID: 39711334
- PMCID: PMC11848338
- DOI: 10.1002/alz.14458
Diagnostic accuracy of phosphorylated tau217 in detecting Alzheimer's disease pathology among cognitively impaired and unimpaired: A systematic review and meta-analysis
Abstract
Our review summarizes the diagnostic accuracy of plasma and cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) phosphorylated tau 217 (p-tau217) in detecting amyloid and tau pathology on positron emission tomography (PET). We systematically reviewed studies that reported the diagnostic accuracy of plasma and CSF p-tau217, searching MEDLINE/PubMed, Scopus, and Web of Science through August 2024. The accuracy of p-tau217 in predicting amyloid and tau pathology on PET was evaluated in 30 studies. Both plasma and CSF p-tau217 effectively detect amyloid and tau PET deposition. Plasma p-tau217 showed 82% sensitivity for detecting amyloid and 83% for tau, with 86% and 83% specificity, respectively. CSF p-tau217 had 79% sensitivity for amyloid and 91% for tau, with 91% and 84% specificity. p-tau217 effectively identifies Alzheimer's disease (AD) pathology. Plasma p-tau217 was comparable to CSF p-tau217 in detecting amyloid deposition on PET. Despite being less sensitive for detecting tau deposition on PET, plasma p-tau217 can be an efficient screening tool for underlying AD pathology. HIGHLIGHTS: Plasma phosphorylated tau 217 (p-tau217) serves as a viable biomarker alternative to cerebrospinal fluid p-tau217 due to the strong concordance between their results. Plasma p-tau217 accurately identifies amyloid and tau positron emission tomography (PET) positivity, exhibiting a low rate of false negatives and positives, thereby establishing it as a reliable diagnostic tool for Alzheimer's disease (AD). Plasma p-tau217 demonstrates slightly higher accuracy in predicting amyloid PET positivity compared to tau PET positivity. Plasma p-tau217 demonstrates higher predictive accuracy in detecting AD pathology among cognitively impaired individuals, compared to cognitively unimpaired individuals, suggesting its enhanced utility as a diagnostic biomarker in clinical settings.
Keywords: Alzheimer's disease; amyloid beta positron emission tomography imaging; cerebrospinal fluid biomarkers; diagnostic test accuracy; phosphorylated tau 217; plasma biomarkers; positron emission tomography; tau positron emission tomography imaging.
© 2025 The Author(s). Alzheimer's & Dementia published by Wiley Periodicals LLC on behalf of Alzheimer's Association.
Conflict of interest statement
G.C. receives consulting fees from Life Molecular Imaging and speaker honoraria from Efficient CME and PeerView. K.C. receives consulting fees from Shanghai Green Valley Pharmaceutical, ADMdx, and Banner Alzheimer's Institute. M.K., K.S., L.M., Y.L., L.Z., T.B., W.D., K.W., N.F., L.G., M.d.L., S.H., Q.R., K.X., S.B., and S.P. report no competing interests. Author disclosures are available in the supporting information.
Figures
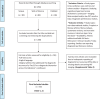

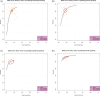
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- R01 HL111724/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 NS104364/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- WCM Neurodegeneration Research Award
- R01AG078800/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- R21 AG087400/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- NARSAD Brain and Behavior Research Foundation
- R01 AG077576/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- Department of Defense
- R01AG080011/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- Red Abbey Labs
- AG077576/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AG057681/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AG085972/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- Minoryx Therapeutics
- P30 AG072980/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AG068398/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AG072794/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AG078800/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- NS104364/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- HL111724/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- U01 AG082845/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AG080011/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- R01AG072794/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- R01AG068398/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

