This is a preprint.
The impact of chronic intermittent hypoxia on enzymatic activity in memory-associated brain regions of male and female rats
- PMID: 39711575
- PMCID: PMC11661378
- DOI: 10.21203/rs.3.rs-5449794/v1
The impact of chronic intermittent hypoxia on enzymatic activity in memory-associated brain regions of male and female rats
Update in
-
The impact of chronic intermittent hypoxia on enzymatic activity in memory-associated brain regions of male and female rats.Biol Sex Differ. 2025 Jan 31;16(1):5. doi: 10.1186/s13293-025-00688-6. Biol Sex Differ. 2025. PMID: 39891225 Free PMC article.
Abstract
Background: Obstructive sleep apnea (OSA) is an intermittent hypoxia disorder associated with cognitive dysfunction, including learning and memory impairments. There is evidence that alterations in protease activity and neuronal activation as associated with cognitive dysfunction, are dependent on sex, and may be brain region-specific. However, the mechanisms mediating OSA-induced cognitive impairments are unclear. Therefore, we used a rat model of OSA, chronic intermittent hypoxia (CIH), to investigate protease activity (e.g., calpain and caspase-3) and neuronal activation (early growth response protein 1, EGR-1) in brain regions associated with learning and memory. We used a rat model of OSA known as chronic intermittent hypoxia (CIH) to investigate protease activity (calpain and caspase-3) and neuronal activation (early growth response protein 1, EGR-1) in brain regions associated with learning and memory.
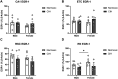
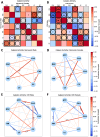
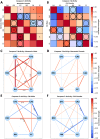
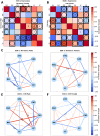
Methods: Male and female Sprague Dawley rats were exposed to CIH or room air (normoxic) for 14 days. We quantified protease activity and cleaved spectrin products, along with EGR-1 protein expression in hippocampal subregions (CA1, CA3), cortical regions [entorhinal cortex (ETC), retrosplenial cortex (RSC), cerebellar cortex (CC)], and subcortical regions [raphe nucleus (RN), locus coeruleus (LC)] associated with learning and memory. Within each group, Pearson correlations of calpain activity, caspase-3 activity, and EGR-1 expression were performed between brain regions. Sex differences within normoxic and CIH correlations were examined.
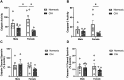
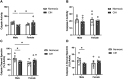
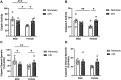
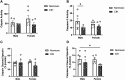
Results: CIH dysregulated calpain activity in male ETC and female CA1 and RSC. CIH dysregulated caspase-3 activity in male RN and female CA1 and RSC. CIH decreased calpain and caspase-3 cleavage products in male ETC. CIH decreased calpain-cleaved spectrin in male RSC but increased these products in female RSC. EGR-1 expression was decreased in male and female RN. Correlational analysis revealed CIH increased excitatory connections in males and increased inhibitory connections in females. EGR-1 expression in males shifted from negative to positive correlations.
Conclusions: Overall, these data show that CIH dysregulates protease activity and impairs neuronal function in a brain region- and sex-dependent manner. This indicates that males and females exhibit sex-specific vulnerabilities to mild OSA. These findings concur with our previous behavioral studies that demonstrated memory impairment in CIH-exposed rats.
Keywords: calpain; caspase-3; chronic intermittent hypoxia; early growth response protein 1; sex differences.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing Interests: Rebecca L. Cunningham is the associate editor of Biology of Sex Differences. No conflicts of interest, financial or otherwise, are disclosed by the remaining authors.
Figures
Similar articles
-
The impact of chronic intermittent hypoxia on enzymatic activity in memory-associated brain regions of male and female rats.Biol Sex Differ. 2025 Jan 31;16(1):5. doi: 10.1186/s13293-025-00688-6. Biol Sex Differ. 2025. PMID: 39891225 Free PMC article.
-
Sex-dependent effects of chronic intermittent hypoxia: implication for obstructive sleep apnea.Biol Sex Differ. 2024 Apr 25;15(1):38. doi: 10.1186/s13293-024-00613-3. Biol Sex Differ. 2024. PMID: 38664845 Free PMC article.
-
Sex and age differences in social and cognitive function in offspring exposed to late gestational hypoxia.Biol Sex Differ. 2023 Nov 11;14(1):81. doi: 10.1186/s13293-023-00557-0. Biol Sex Differ. 2023. PMID: 37951901 Free PMC article.
-
Sex differences in the respiratory-sympathetic coupling in rats exposed to chronic intermittent hypoxia.Respir Physiol Neurobiol. 2018 Oct;256:109-118. doi: 10.1016/j.resp.2017.09.003. Epub 2017 Sep 8. Respir Physiol Neurobiol. 2018. PMID: 28893610 Review.
-
Effect of chronic intermittent hypoxia on gene expression profiles of rat liver: a better understanding of OSA-related liver disease.Sleep Breath. 2020 Jun;24(2):761-770. doi: 10.1007/s11325-019-01987-0. Epub 2019 Dec 16. Sleep Breath. 2020. PMID: 31845084 Review.
References
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

