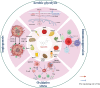
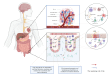
From nature to clinic: Quercetin's role in breast cancer immunomodulation
- PMID: 39712006
- PMCID: PMC11659267
- DOI: 10.3389/fimmu.2024.1483459
From nature to clinic: Quercetin's role in breast cancer immunomodulation
Abstract
Immunotherapy has brought hope to many breast cancer patients, but not all patients benefit from it. Quercetin (Qu), a natural product found in various sources, has anti-inflammatory and anti-tumor properties. We conducted a review of the pharmacological research of Qu in regulating anti-tumor immunity in vivo and in vitro. Qu can directly regulate the local tumor microenvironment (TME) by enhancing the activity of immune cells which includes promoting the infiltration of T cells and natural killer (NK) cells, inhibiting the recruitment of myeloid-derived suppressor cells and tumor-associated macrophages. Additionally, Qu inhibits anaerobic glycolysis in tumor cells, thereby reducing the production and transport of lactic acid. It also suppresses tumor angiogenesis by targeting the vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) pathway and the vitamin D pathway. Furthermore, Qu can enhance the efficacy of immunotherapy for breast cancer by modulating the systemic microenvironment. This includes inhibiting obesity-related chronic inflammation to decrease the production of inflammatory factors, regulating the composition of intestinal microbiota, and intervening in the metabolism of intestinal flora. At the same time, we also address challenges in the clinical application of Qu, such as low absorption rates and unknown effective doses. In conclusion, we highlight Qu as a natural immunomodulator that enhances immune cell activity and has the potential to be developed as an adjunct for breast cancer.
Keywords: Quercetin; breast cancer; immunotherapy; natural immunomodulator; tumor immune microenvironment.
Copyright © 2024 Fang, Gao, Wang, Zhao, Zhang and Wang.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Quercetin inhibits angiogenesis by targeting calcineurin in the xenograft model of human breast cancer.Eur J Pharmacol. 2016 Jun 15;781:60-8. doi: 10.1016/j.ejphar.2016.03.063. Epub 2016 Apr 1. Eur J Pharmacol. 2016. PMID: 27041643
-
Gold nanoparticle-conjugated quercetin inhibits epithelial-mesenchymal transition, angiogenesis and invasiveness via EGFR/VEGFR-2-mediated pathway in breast cancer.Cell Prolif. 2016 Dec;49(6):678-697. doi: 10.1111/cpr.12296. Epub 2016 Sep 18. Cell Prolif. 2016. PMID: 27641938 Free PMC article.
-
Reprogramming the breast tumor immune microenvironment: cold-to-hot transition for enhanced immunotherapy.J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 2025 Apr 25;44(1):131. doi: 10.1186/s13046-025-03394-8. J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 2025. PMID: 40281554 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Augmenting Anticancer Immunity Through Combined Targeting of Angiogenic and PD-1/PD-L1 Pathways: Challenges and Opportunities.Front Immunol. 2020 Nov 5;11:598877. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2020.598877. eCollection 2020. Front Immunol. 2020. PMID: 33250900 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Gold nanoparticles-conjugated quercetin induces apoptosis via inhibition of EGFR/PI3K/Akt-mediated pathway in breast cancer cell lines (MCF-7 and MDA-MB-231).Cell Biochem Funct. 2017 Jun;35(4):217-231. doi: 10.1002/cbf.3266. Epub 2017 May 12. Cell Biochem Funct. 2017. PMID: 28498520
Cited by
-
Quercetin: A Natural Ally in Combating Breast Cancer.Int J Nanomedicine. 2025 Jul 19;20:9155-9177. doi: 10.2147/IJN.S518174. eCollection 2025. Int J Nanomedicine. 2025. PMID: 40708864 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Quercetin as a therapeutic agent for acute pancreatitis: a comprehensive review of antioxidant, anti-inflammatory, and immunomodulatory mechanisms.Front Pharmacol. 2025 Apr 28;16:1587314. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2025.1587314. eCollection 2025. Front Pharmacol. 2025. PMID: 40356955 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Quercetin as a multi-targeted therapeutic agent in breast cancer: molecular targets and therapeutic potential.Med Oncol. 2025 Jul 22;42(8):365. doi: 10.1007/s12032-025-02907-x. Med Oncol. 2025. PMID: 40694163 Review.
-
Therapeutic Role of Quercetin in Prostate Cancer: A Study of Network Pharmacology, Molecular Docking, and Dynamics Simulation.Cell Biochem Biophys. 2025 Feb 19. doi: 10.1007/s12013-025-01697-3. Online ahead of print. Cell Biochem Biophys. 2025. PMID: 39966335
-
Exploring the Mechanism of Lianqiao Jinbei Decoction Inhibiting HER2-Positive Breast Cancer Based on Network Pharmacology and Experimental Verification.Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press). 2025 Jul 14;17:583-598. doi: 10.2147/BCTT.S522528. eCollection 2025. Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press). 2025. PMID: 40686518 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical