Crystal structure, Hirshfeld surface analysis, and DFT and mol-ecular docking studies of 6-cyanona-phthalen-2-yl 4-(benz-yloxy)benzoate
- PMID: 39712165
- PMCID: PMC11660483
- DOI: 10.1107/S2056989024009964
Crystal structure, Hirshfeld surface analysis, and DFT and mol-ecular docking studies of 6-cyanona-phthalen-2-yl 4-(benz-yloxy)benzoate
Abstract
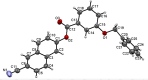
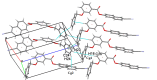
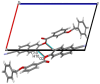
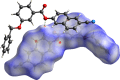
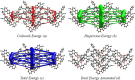
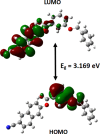
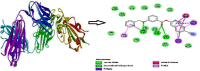
In the title compound, C25H17NO3, the torsion angle associated with the phenyl benzoate group is -173.7 (2)° and that for the benz-yloxy group is -174.8 (2)° establishing an anti-type conformation. The dihedral angles between the ten-membered cyanona-phthalene ring and the aromatic ring of the phenyl benzoate and the benz-yloxy fragments are 40.70 (10) and 87.51 (11)°, respectively, whereas the dihedral angle between the aromatic phenyl benzoate and the benz-yloxy fragments is 72.30 (13)°. In the crystal, the mol-ecules are linked by weak C-H⋯O inter-actions forming S(4) chains propagating parallel to [010]. The packing is consolidated by three C-H⋯π inter-actions and two π-π stacking inter-actions between the aromatic rings of naphthalene and phenyl benzoate with centroid-to-centroid distances of 3.9698 (15) and 3.8568 (15) Å, respectively. Inter-molecular inter-actions were qu-anti-fied using Hirshfeld surface analysis. The mol-ecular structure was further optimized by density functional theory (DFT) at the B3LYP/6-311+ G(d,p) level, revealing that the energy gap between HOMO and LUMO is 3.17 eV. Mol-ecular docking studies were carried out for the title compound as a ligand and SARS-Covid-2(PDB ID:7QF0) protein as a receptor giving a binding affinity of -9.5 kcal mol-1.
Keywords: 4-(benzyloxy)benzoate; DFT; Hirshfeld surface; crystal structure; cyanonapthalene and molecular docking; intermolecular interactions.
© Harish Kumar et al. 2024.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Crystal structure, Hirshfeld surface analysis, DFT and mol-ecular docking studies of 4'-(benz-yloxy)-[1,1'-biphen-yl]-3-carb-oxy-lic acid.Acta Crystallogr E Crystallogr Commun. 2025 Feb 11;81(Pt 3):208-213. doi: 10.1107/S2056989025001021. eCollection 2025 Mar 1. Acta Crystallogr E Crystallogr Commun. 2025. PMID: 40071035 Free PMC article.
-
Crystal structure, Hirshfeld surface analysis, DFT and mol-ecular docking investigation of 2-(2-oxo-1,3-oxazolidin-3-yl)ethyl 2-[2-(2-oxo-1,3-oxazolidin-3-yl)eth-oxy]quinoline-4-carboxyl-ate.Acta Crystallogr E Crystallogr Commun. 2021 Jan 1;77(Pt 1):28-33. doi: 10.1107/S2056989020015960. eCollection 2021 Jan 1. Acta Crystallogr E Crystallogr Commun. 2021. PMID: 33520278 Free PMC article.
-
Synthesis, crystal structure and Hirshfeld surface analysis of 4'-cyano-[1,1'-biphen-yl]-4-yl 3-(benz-yloxy)benzoate.Acta Crystallogr E Crystallogr Commun. 2024 Sep 12;80(Pt 10):1010-1013. doi: 10.1107/S2056989024008570. eCollection 2024 Sep 1. Acta Crystallogr E Crystallogr Commun. 2024. PMID: 39372188 Free PMC article.
-
Synthesis, crystal structure and Hirshfeld surface analysis of naphthalene-2,3-diyl bis-(3-benz-yl-oxy)benzoate.Acta Crystallogr E Crystallogr Commun. 2023 Jul 4;79(Pt 8):686-689. doi: 10.1107/S2056989023005571. eCollection 2023 Jul 1. Acta Crystallogr E Crystallogr Commun. 2023. PMID: 37601398 Free PMC article.
-
Crystal structure, Hirshfeld surface analysis, DFT and mol-ecular docking studies of ethyl 5-amino-2-bromo-isonicotinate.Acta Crystallogr E Crystallogr Commun. 2024 Nov 8;80(Pt 12):1274-1279. doi: 10.1107/S2056989024010594. eCollection 2024 Nov 1. Acta Crystallogr E Crystallogr Commun. 2024. PMID: 39906785 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Synthesis, crystal structure, Hirshfeld surface analysis, density function theory calculations and photophysical properties of methyl 4'-[(4-bromobenzo-yl)-oxy]biphenyl-4-carboxyl-ate: a compound with bromine⋯oxygen contacts.Acta Crystallogr E Crystallogr Commun. 2025 Feb 28;81(Pt 3):264-270. doi: 10.1107/S2056989025001604. eCollection 2025 Mar 1. Acta Crystallogr E Crystallogr Commun. 2025. PMID: 40071042 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Baya, M., Belío, Ú., Forniés, J., Martín, A., Perálvarez, M. & Sicilia, V. (2015). Inorg. Chim. Acta, 424, 136–149.
-
- Bernstein, J., Davis, R. E., Shimoni, L. & Chang, N.-L. (1995). Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. Engl.34, 1555–1573.
-
- Biovia (2017). Discovery Studio Visualizer. Biovia, San Diego, CA, USA.
-
- Boyle, E. A., Freemanm, P. C., Mangan, F. R. & Thomson, M. J. (1982). J. Pharm. Pharmacol.34, 562–569. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
