Two detoxification enzyme genes, CYP6DA2 and CarFE4, mediate the susceptibility to afidopyropen in Semiaphis heraclei
- PMID: 39712191
- PMCID: PMC11659293
- DOI: 10.3389/fphys.2024.1478869
Two detoxification enzyme genes, CYP6DA2 and CarFE4, mediate the susceptibility to afidopyropen in Semiaphis heraclei
Abstract
Introduction: Semiaphis heraclei is an important economic pest affecting Caprifoliaceae and Apiaceae plants, and chemical control is still the main effective control method in the field. Afidopyropen is a new type of pyridine cyclopropyl insecticide, which can effectively control piercing-sucking mouthparts pests and is suitable for pest resistance management. However, the detoxification mechanism of S. heraclei to afidopyropen is still poorly cleared.
Methods: The insecticidal activity of afidopyropen against S. heraclei and the enzyme activity assay and synergism bioassay were evaluated. The detoxification enzyme genes were obtained by transcriptome and validated by quantitative real-time PCR (RT-qPCR). Furthermore, RNA interference was used to study the functions of detoxification enzyme genes.
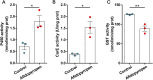
Results: The activities of cytochrome P450 monooxygenases (P450s) and carboxylesterases (CarEs) were significantly increased under afidopyropen treatment. The toxicity of afidopyropen against S. heraclei was significantly increased after application the inhibitors of piperonyl butoxide and triphenyl phosphate. Sixteen P450 genes and three CarE genes were identified in the transcriptome of S. heraclei. The RT-qPCR results showed that eleven P450 genes and two CarE genes were significantly upregulated under afidopyropen treatment, and the expression of CYP6DA2 and CarFE4 was upregulated by more than 2.5 times. The expression pattern of CYP6DA2 and CarFE4 was further analyzed in different developmental stages of S. heraclei and knockdown of CYP6DA2 and CarFE4 significantly increased the susceptibility of S. heraclei to afidopyropen.
Conclusion: The results of this study uncover the key functions of CYP6DA2 and CarFE4 in the detoxification mechanism of S. heraclei to afidopyropen, and provide a theoretical basis for the scientific use of afidopyropen in the field.
Keywords: CYP6DA2; CarFE4; Semiaphis heraclei; afidopyropen; detoxification mechanism.
Copyright © 2024 Fu, Xue, Wang, Wang, Zhu, Yang, Zhang, Zhou, Zhao, Shan and Zhang.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Knockdown of TRPV gene Nanchung decreases resistance to the novel pyropene insecticide, afidopyropen, in Bemisia tabaci.Int J Biol Macromol. 2023 Jan 1;224:1566-1575. doi: 10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2022.10.242. Epub 2022 Oct 28. Int J Biol Macromol. 2023. PMID: 36330856
-
Characterization of Field-Evolved Resistance to Afidopyropen, a Novel Insecticidal Toxin Developed from Microbial Secondary Metabolites, in Bemisia tabaci.Toxins (Basel). 2022 Jul 1;14(7):453. doi: 10.3390/toxins14070453. Toxins (Basel). 2022. PMID: 35878191 Free PMC article.
-
Function Analysis of P450 and GST Genes to Imidacloprid in Aphis craccivora (Koch).Front Physiol. 2021 Jan 20;11:624287. doi: 10.3389/fphys.2020.624287. eCollection 2020. Front Physiol. 2021. PMID: 33551847 Free PMC article.
-
Comparative analysis of the detoxification gene inventory of four major Spodoptera pest species in response to xenobiotics.Insect Biochem Mol Biol. 2021 Nov;138:103646. doi: 10.1016/j.ibmb.2021.103646. Epub 2021 Aug 29. Insect Biochem Mol Biol. 2021. PMID: 34469782 Review.
-
RNA interference: Applications and advances in insect toxicology and insect pest management.Pestic Biochem Physiol. 2015 May;120:109-17. doi: 10.1016/j.pestbp.2015.01.002. Epub 2015 Jan 9. Pestic Biochem Physiol. 2015. PMID: 25987228 Review.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

