Role of conscious awareness and Big Five in predicting the digital addiction
- PMID: 39712296
- PMCID: PMC11659781
- DOI: 10.3389/fpubh.2024.1449847
Role of conscious awareness and Big Five in predicting the digital addiction
Abstract
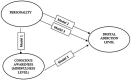
Introduction: Digital addiction is discussed in the literature as a type of addiction that negatively affects the personal, social, and societal lives of individuals. Digital addiction is a behavioral addiction that occurs as a result of the problematic and unconscious use of digital tools with features such as compulsive, excessive, impulsivity, and includes human-machine interaction. What is meant to be expressed with conscious awareness is to accept the facts and experiences as they are without judgment, and to be aware of them. With awareness, it is aimed to contribute to individuals to evaluate their past experiences more objectively, to get rid of automatic behavioral and emotional patterns, and to show more moderate reactions by avoiding aggressive reactions. In this context, this study examines the Big Five and Mindfulness as predictive variables for digital addiction, focusing on them as a cause and a solution variable that can be used in interventions for digital addiction. Given its prevalence and negative effects, it is important to identify and analyze the relationship patterns between digital addiction and related variables in order to define and resolve the problem. In this context, the present study aims to determine the levels of conscious awareness and digital addiction among university students and to examine the predictive effect of conscious awareness levels and Big Five variables on predicting digital addiction behaviors.
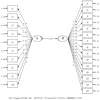
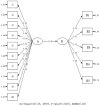
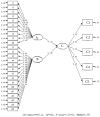
Methods: The present study is designed to employ the survey method. Data were collected from 1,664 university students selected by using the convenience sampling method, and the data obtained were analyzed by using descriptive statistics and structural equation modeling. The SPSS 25 and LISREL 8.8 software packages were used in the analysis process.
Results and discussion: The results achieved in this study revealed that university students have a moderate level of conscious awareness and that the overall level of digital addiction is generally moderate. The results achieved from the structural equation modeling for the measurement model constructed for the relationships between variables confirmed the validity of the proposed model. It was determined that the model had a good fit with the latent variables, which represent the indicator variables, and also other latent variables. In conclusion, it was found that Big Five and the level of conscious awareness have a reducing effect on digital addiction and serve a protective function against this negativity among university students.
Keywords: Big Five; behavioral addiction; conscious awareness (mindfulness); digital addiction; personality.
Copyright © 2024 Erzincanli and Geçikli.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Ruberto V., Toto G., Toto M. (2018). Technologies: a comparison between negative aspects of addictions and effects on text comprehension. 31st international-business-information-management-association conference. (6380–6390). Milan, Italy: Int Business Informat Management.
-
- Bueso VG, Santamaría JJ, Fernández D, Merino L, Alvarado EM, Murcia SJ, et al. Internet gaming disorder in adolescents: personality, psychopathology and evaluation of a psychological ıntervention combined with parent psychoeducation. Front Psychol. (2018) 9:787. doi: 10.3389/fpsyg.2018.00787, PMID: - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Griffiths MDL. Recent innovations in video game addiction research and theory. Global Media J. (2010) 4:1–13.
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

