Exploring the impact of deubiquitination on melanoma prognosis through single-cell RNA sequencing
- PMID: 39712483
- PMCID: PMC11659643
- DOI: 10.3389/fgene.2024.1509049
Exploring the impact of deubiquitination on melanoma prognosis through single-cell RNA sequencing
Abstract
Background: Cutaneous melanoma, characterized by the malignant proliferation of melanocytes, exhibits high invasiveness and metastatic potential. Thus, identifying novel prognostic biomarkers and therapeutic targets is essential.
Methods: We utilized single-cell RNA sequencing data (GSE215120) from the Gene Expression Omnibus (GEO) database, preprocessing it with the Seurat package. Dimensionality reduction and clustering were executed through Principal Component Analysis (PCA) and Uniform Manifold Approximation and Projection (UMAP). Cell types were annotated based on known marker genes, and the AUCell algorithm assessed the enrichment of deubiquitination-related genes. Cells were categorized into DUB_high and DUB_low groups based on AUCell scores, followed by differential expression analysis. Importantly, we constructed a robust prognostic model utilizing various genes, which was evaluated in the TCGA cohort and an external validation cohort.
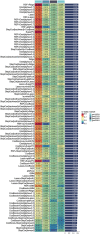
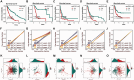
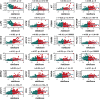
Results: Our prognostic model, developed using Random Survival Forest (RSF) and Ridge Regression methods, demonstrated excellent predictive performance, evidenced by high C-index and AUC values across multiple cohorts. Furthermore, analyses of immune cell infiltration and tumor microenvironment scores revealed significant differences in immune cell distribution and microenvironment characteristics between high-risk and low-risk groups. Functional experiments indicated that TBC1D16 significantly impacts the migration and proliferation of melanoma cells.
Conclusion: This study highlights the critical role of deubiquitination in melanoma and presents a novel prognostic model that effectively stratifies patient risk. The model's strong predictive ability enhances clinical decision-making and provides a framework for future studies on the therapeutic potential of deubiquitination mechanisms in melanoma progression. Further validation and exploration of this model's applicability in clinical settings are warranted.
Keywords: deubiquitination; immune microenvironment; melanoma; prognostic model; single-cell RNA sequencing.
Copyright © 2024 Peng, Xie and He.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Integrative analysis of bulk and single-cell RNA-seq reveals the molecular characterization of the immune microenvironment and oxidative stress signature in melanoma.Heliyon. 2024 Mar 15;10(6):e28244. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2024.e28244. eCollection 2024 Mar 30. Heliyon. 2024. PMID: 38560689 Free PMC article.
-
The fatty acid-related gene signature stratifies poor prognosis patients and characterizes TIME in cutaneous melanoma.J Cancer Res Clin Oncol. 2024 Jan 27;150(2):40. doi: 10.1007/s00432-023-05580-7. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol. 2024. PMID: 38279987 Free PMC article.
-
Analysis on tumor immune microenvironment and construction of a prognosis model for immune-related skin cutaneous melanoma.Zhong Nan Da Xue Xue Bao Yi Xue Ban. 2023 May 28;48(5):671-681. doi: 10.11817/j.issn.1672-7347.2023.230069. Zhong Nan Da Xue Xue Bao Yi Xue Ban. 2023. PMID: 37539569 Free PMC article. Chinese, English.
-
Unravelling the metabolic landscape of cutaneous melanoma: Insights from single-cell sequencing analysis and machine learning for prognostic assessment of lactate metabolism.Exp Dermatol. 2024 Jun;33(6):e15119. doi: 10.1111/exd.15119. Exp Dermatol. 2024. PMID: 38881438
-
Comprehensive analysis of scRNA-Seq and bulk RNA-Seq reveals dynamic changes in the tumor immune microenvironment of bladder cancer and establishes a prognostic model.J Transl Med. 2023 Mar 27;21(1):223. doi: 10.1186/s12967-023-04056-z. J Transl Med. 2023. PMID: 36973787 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Bogunovic D., O'Neill D. W., Belitskaya-Levy I., Vacic V., Yu Y. L., Adams S., et al. (2009). Immune profile and mitotic index of metastatic melanoma lesions enhance clinical staging in predicting patient survival. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A. 106 (48), 20429–20434. 10.1073/pnas.0905139106 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

