Protective effect of Haoqin Qingdan decoction on pulmonary and intestinal injury in mice with influenza viral pneumonia
- PMID: 39712501
- PMCID: PMC11658977
- DOI: 10.3389/fphar.2024.1449322
Protective effect of Haoqin Qingdan decoction on pulmonary and intestinal injury in mice with influenza viral pneumonia
Abstract
Background: Haoqin Qingdan decoction (HQQD), composed of eleven herbs, is a traditional Chinese formula widely recognized for its efficacy in treating pulmonary inflammation induced by viral infections. Despite its extensive use, the potential pulmonary and intestinal protective effects of HQQD on influenza viral pneumonia (IVP) and the underlying molecular mechanisms remain unclear.
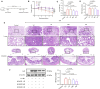
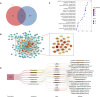
Materials and methods: Ultra-high-performance liquid chromatography coupled with mass spectrometry (UHPLC-MS) was employed to identify the major chemical constituents of the prescription. Subsequently, network analysis was conducted to predict the potential therapeutic targets of HQQD in IVP. The mechanisms by which HQQD mitigates lung and intestinal damage were further elucidated by assessing NP protein expression, inflammatory factors, TLR7/MyD88/NF-κB signaling pathway mRNAs and proteins, and through intestinal flora analysis.
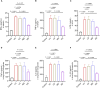
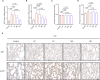
Results: The protective effects of HQQD on pulmonary and intestinal injuries induced by IVP were thoroughly investigated using comprehensive network analysis, signaling pathway validation, and gut microflora analysis. UHPLC-MS analysis identified the primary chemical constituents. Validation experiments demonstrated a significant reduction in NP protein expression in the lungs. HQQD notably alleviated immune damage in the lungs and intestines of mice by inhibiting NP protein expression and the release of inflammatory factors such as interleukin-6 (IL-6), interleukin-1β (IL-1β), tumor necrosis factor-alpha (TNF-α) and interferon-gamma (IFN-γ); downregulating the expression levels of TLR7, MyD88, and phospho-NF-κB p65 (p-p65); lowering serum LPS levels; and reducing the relative abundance of Proteobacteria.
Conclusion: HQQD exerts therapeutic effects against influenza viral pneumonia through antiviral and anti-inflammatory mechanisms and by remodeling the intestinal flora. This study provides initial insights into the "gut-lung" axis mechanism of HQQD in combating respiratory influenza virus infection.
Keywords: Haoqin Qingdan decoction; influenza viral pneumonia; intestinal flora; network analysis; traditional Chinese medicine.
Copyright © 2024 Lin, Lin, Ji, Zhang, Zhang, Hong, Li and Lin.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest. The reviewer PX declared a shared affiliation with the authors to the handling editor at the time of review.
Figures

References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

