Assessment of the diagnostic value of serum cathepsin S and its correlation with HDL subclasses in patients with non-Hodgkin's lymphoma
- PMID: 39712508
- PMCID: PMC11662951
- DOI: 10.5937/jomb0-48959
Assessment of the diagnostic value of serum cathepsin S and its correlation with HDL subclasses in patients with non-Hodgkin's lymphoma
Abstract
Background: Recent findings point to the key role of cathepsin S (CTSS) in the survival of malignant cells, as well as the significance of the anti-apoptotic properties of high-density lipoprotein (HDL) that contribute to enhanced cell survival. The purpose of this study is to analyse CTSS as a potential biomarker in lymphoma. Also, in order to better understand the role of CTSS in the origin and development of lymphoma, its association with cystatin C (Cys C), lipids, and inflammatory markers was analysed.
Methods: The study included 90 subjects: 11 Hodgkin (HL) and 44 B-cell non-Hodgkin lymphoma (NHL) patients, as well as 35 healthy subjects. CTSS was determined using the Invitrogen ELISA kit (Thermo Fisher Scientific, Inc., Waltham, MA, USA). The non-denaturing 3%-31% polyacrylamide gradient gel electrophoresis method was used to separate plasma HDL particles.
Results: The level of CTSS was significantly higher in NHL patients than in control subjects: 12.20 (9.75-14.57) vs 9.97 (8.44-10.99), P<0.001. In NHL patients, there was a positive correlation between CTSS and the proportions of HDL3a, HDL3b, and the sum of the HDL3 subclasses (r=0.506, P<0.001; r=0.411, P=0.006, r=0.335, P=0.026, respectively). In addition, the area under the receiver operating characteristic curve (AUC curve) of CTSS was 0.766 (CI: 0.655-0.856) for NHL patients. There was no significant difference in CTSS values between the control group and patients with HL, nor significant correlations between CTSS and HDL subclasses in the HL group.
Conclusions: CTSS is significantly elevated in patients with NHL and has the potential to be a new diagnostic bio - marker for the detection of NHL. Also, this study was the first to unveil the association between serum CTSS levels and the proportions of anti-apoptotic HDL3a and HDL3b subclasses in NHL patients.
Uvod: Novija otkrića ukazuju na ključnu ulogu katepsina S (CTSS) u preživljavanju malignih ćelija, kao i na značaj anti-apoptotičkih osobina lipoproteina visoke gustoće (HDL) koje doprinose većem preživljavanja ćelija. Cilj ove studije je analizirati CTSS kao potencijalni biomarker kod limfomu. Takođe, kako bi se bolje razumela uloga CTSS-a u nastanku i razvoju limfoma, analizirana je njegova povezanost sa cistatinom C (Cys C), lipidima i upalnim markerima.
Metode: U istraživanje je bilo uključeno 90 ispitanika: 11 bolesnika sa Hodgkinovim (HL) i 44 bolesnika sa B-ćelijskim ne-Hodgkinovim limfomom (NHL), te 35 zdravih ispitanika. Za merenje serumskog CTSS je korišćen Invitrogen ELISA kit (Thermo Fisher Scientific, Inc., Waltham, MA, SAD). HDL subfrakcije su razdvojene metodom vertikalne elektroforeze na gradijentu poliakrilamida.
Rezultati: Nivo CTSS bio je značajno viši kod pacijenata sa NHL-om nego kod ispitanika kontrolne grupe: 12,20 (9,75-14,57) naspram 9,97 (8,44-10,99), P<0,001. Takođe, kod pacijenata s NHL-om postojala je pozitivna korelacija između CTSS i proporcije HDL3a, HDL3b i HDL3 potklasa (r=0,506, P<0,001; r=0,411, P=0,006, r=0,335, P =0,026). Osim toga, površina ispod ROC krive (AUC) CTSS bila je 0,766 (CI: 0,655-0,856) za NHL pacijente. Nije bilo značajne razlike u vrednostima CTSS između kontrolne grupe i pacijenata sa HL-om, kao niti značajnih korelacija između CTSS i HDL podklasa.
Zaključak: CTSS je bio značajno povišen kod pacijenata sa NHL što pokazuje da CTSS ima potencijal novog dijagnostičkog biomarkera za otkrivanje NHL. Takođe, ovo istraživanje je prvo koje je pokazalo da postoji korelacija između serumskog CTSS i udela anti-apoptotskih podklasa HDL3a i HDL3b kod pacijenata s NHL-om.
Keywords: HDL3a and HDL3b sub classes; Hodgkin and non-Hodgkin lymphoma; apoptosis; cathepsin S; cystatin C.
2024 Bosa Mirjanić-Azarić, Siniša Stanković, Zana Radić-Savić, Dragana Malčić-Zanić, Ana Ninić, Marija Vuković, Lana Nezić, Ranko Skrbić, Nataša Bogavac-Stanojević, published by CEON/CEES.
Conflict of interest statement
All the authors declare that they have no conflict of interest in this work.Conflict of Interest: The authors stated that they have no conflicts of interest regarding the publication of this article.
Figures

Abbreviations: AUC, the area under the ROC curve; CTSS, cathepsin S; LDH, lactate dehydrogenase; CRP, C-reactive protein
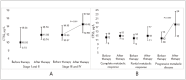
Figure 2 A, according to disease stages; Figure 2 B according to response to therapy Abbreviation: CTSS, cathepsin S.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous
