Radiomics analysis of thoracic vertebral bone marrow microenvironment changes before bone metastasis of breast cancer based on chest CT
- PMID: 39712652
- PMCID: PMC11655691
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jbo.2024.100653
Radiomics analysis of thoracic vertebral bone marrow microenvironment changes before bone metastasis of breast cancer based on chest CT
Abstract
Bone metastasis from breast cancer significantly elevates patient morbidity and mortality, making early detection crucial for improving outcomes. This study utilizes radiomics to analyze changes in the thoracic vertebral bone marrow microenvironment from chest computerized tomography (CT) images prior to bone metastasis in breast cancer, and constructs a model to predict metastasis.
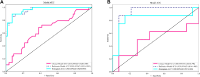
Methods: This study retrospectively gathered data from breast cancer patients who were diagnosed and continuously monitored for five years from January 2013 to September 2023. Radiomic features were extracted from the bone marrow of thoracic vertebrae on non-contrast chest CT scans. Multiple machine learning algorithms were utilized to construct various radiomics models for predicting the risk of bone metastasis, and the model with optimal performance was integrated with clinical features to develop a nomogram. The effectiveness of this combined model was assessed through receiver operating characteristic (ROC) analysis as well as decision curve analysis (DCA).
Results: The study included a total of 106 patients diagnosed with breast cancer, among whom 37 developed bone metastases within five years. The radiomics model's area under the curve (AUC) for the test set, calculated using logistic regression, is 0.929, demonstrating superior predictive performance compared to alternative machine learning models. Furthermore, DCA demonstrated the potential of radiomics models in clinical application, with a greater clinical benefit in predicting bone metastasis than clinical model and nomogram.
Conclusion: CT-based radiomics can capture subtle changes in the thoracic vertebral bone marrow before breast cancer bone metastasis, offering a predictive tool for early detection of bone metastasis in breast cancer.
Keywords: Bone marrow microenvironment; Bone metastasis; Breast cancer; Radiomics; Tomography; X-ray computed.
© 2024 The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
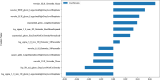
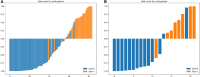
Figures





References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

