Comparing the Effects of Propofol and Thiopental on Human Renal HEK-293 Cells With a Focus on Reactive Oxygen Species (ROS) Production, Cytotoxicity, and Apoptosis: Insights Into Dose-Dependent Toxicity
- PMID: 39712718
- PMCID: PMC11663022
- DOI: 10.7759/cureus.74120
Comparing the Effects of Propofol and Thiopental on Human Renal HEK-293 Cells With a Focus on Reactive Oxygen Species (ROS) Production, Cytotoxicity, and Apoptosis: Insights Into Dose-Dependent Toxicity
Abstract
Objectives: Propofol and thiopental are widely used as hypnotic, sedative, antiepileptic, and analgesic agents in general anesthesia and intensive care; however, their side effects remain unknown. They are used for long periods and at high doses for sedation in total intravenous anesthesia (TIVA) and intensive care units. Long-term and high-dose use of these drugs can lead to accumulation in plasma and tissues, resulting in high drug concentrations and increasing the risk of potential toxicity (e.g., nephrotoxicity). In our study, the cytotoxic and apoptotic effects of propofol and thiopental on kidney cells (HEK-293) and their effects on the formation of reactive oxygen species (ROS) when used in high doses were investigated and compared in vitro.
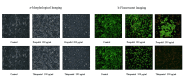
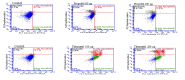
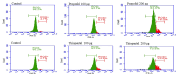
Materials and methods: The half-maximal inhibitory concentration (IC50) of each drug in HEK-293 cells was determined using the 3-(4,5-dimethylthiazol-2-yl)-2,5-diphenyltetrazolium bromide method. The apoptotic effects were assessed at two different doses of each drug using the annexin V method. Morphological examinations were conducted using the acridine orange/ethidium bromide method, and intracellular ROS levels were determined by flow cytometry.
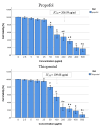
Results: The IC50 values of propofol and thiopental for HEK-293 cells were 206.59 μg/ml and 109.68 μg/ml, respectively. Compared to the control group, thiopental at ≥25 μg/ml and propofol at ≥50 μg/ml exhibited cytotoxicity. Additionally, propofol exhibited significantly lower cytotoxic effects than thiopental did.
Conclusion: Our study showed that both propofol and thiopental exerted significant cytotoxic effects on HEK-293 cells at concentrations exceeding clinical levels, primarily by increasing intracellular ROS levels and inducing apoptosis. Future research in this area will deepen our understanding of these mechanisms and improve patient safety in clinical anesthesia practice.
Keywords: anesthesia; apoptosis; cytotoxicity; human kidney cells (hek-293); propofol-thiopental; reactive oxygen species (ros).
Copyright © 2024, Pehlivan et al.
Conflict of interest statement
Human subjects: All authors have confirmed that this study did not involve human participants or tissue. Animal subjects: All authors have confirmed that this study did not involve animal subjects or tissue. Conflicts of interest: In compliance with the ICMJE uniform disclosure form, all authors declare the following: Payment/services info: This research was supported by the Harran University Scientific Research Projects Unit (HUBAK: 31/12/2019; project number: 19342). Financial relationships: All authors have declared that they have no financial relationships at present or within the previous three years with any organizations that might have an interest in the submitted work. Other relationships: All authors have declared that there are no other relationships or activities that could appear to have influenced the submitted work.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Comparison of cytotoxic, reactive oxygen species (ROS) and apoptotic effects of propofol, thiopental and dexmedetomidine on liver cells at accumulative doses (AML12).Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. 2023 Feb;27(4):1336-1345. doi: 10.26355/eurrev_202302_31367. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. 2023. PMID: 36876672
-
Changes in intraocular pressures during laparoscopy: a comparison of propofol total intravenous anesthesia to desflurane-thiopental anesthesia.Middle East J Anaesthesiol. 2013 Feb;22(1):47-52. Middle East J Anaesthesiol. 2013. PMID: 23833850 Clinical Trial.
-
Phytochemically analysed extract of Ageratina adenophora (Sprengel) R.M.King & H. Rob. initiates caspase 3-dependant apoptosis in colorectal cancer cell: A synergistic approach with chemotherapeutic drugs.J Ethnopharmacol. 2024 Mar 25;322:117591. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2023.117591. Epub 2023 Dec 15. J Ethnopharmacol. 2024. PMID: 38104872
-
Propofol and thiopental for intravenous induction in neonates: Study protocol for a dose-finding trial.Acta Anaesthesiol Scand. 2023 Jul;67(6):820-828. doi: 10.1111/aas.14238. Epub 2023 Jun 2. Acta Anaesthesiol Scand. 2023. PMID: 36919345
-
[Does propofol have advantages over midazolam and isoflurane? Comparative study of 2 total intravenous anesthesia techniques using midazolam and propofol, versus balanced anesthesia with isoflurane].Rev Esp Anestesiol Reanim. 1994 May-Jun;41(3):156-64. Rev Esp Anestesiol Reanim. 1994. PMID: 8059043 Clinical Trial. Spanish.
Cited by
-
Exploring the correlation between Drp1 protein and the neurotoxicity of propofol.Front Neurosci. 2025 Jul 21;19:1614362. doi: 10.3389/fnins.2025.1614362. eCollection 2025. Front Neurosci. 2025. PMID: 40761317 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Update on developmental anesthesia neurotoxicity. Vutskits L, Davidson A. Curr Opin Anaesthesiol. 2017;30:337–342. - PubMed
-
- Review of preclinical studies on pediatric general anesthesia-induced developmental neurotoxicity. Walters JL, Paule MG. Neurotoxicol Teratol. 2017;60:2–23. - PubMed
-
- Folino TB, Muco E, Safadi AO, Parks LJ. StatPearls. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2023. Propofol. - PubMed
-
- Propofol prevents renal ischemia-reperfusion injury via inhibiting the oxidative stress pathways. Li Y, Zhong D, Lei L, Jia Y, Zhou H, Yang B. Cell Physiol Biochem. 2015;37:14–26. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous
