Legionella Pneumonia Undetected by Repeated Urinary Antigen Testing With Ribotest® Legionella
- PMID: 39712728
- PMCID: PMC11661902
- DOI: 10.7759/cureus.74035
Legionella Pneumonia Undetected by Repeated Urinary Antigen Testing With Ribotest® Legionella
Abstract
This report presents a patient with Legionella pneumonia (LP), initially presented with fever and mild hypoxemia, with subsequent progression to severe pneumonia during hospitalization. Despite multiple negative urinary antigen tests using Ribotest® Legionella, the diagnosis was confirmed via the loop-mediated isothermal amplification method of lower respiratory tract secretions. This case highlights the diagnostic limitations of Ribotest® Legionella and emphasizes the importance of a comprehensive diagnostic strategy, incorporating nucleic acid amplification tests or culture in suspected patients with LP. Early recognition of these diagnostic challenges is critical for optimizing patient outcomes.
Keywords: bronchoscopy; legionella pneumonia; loop-mediated isothermal amplification; ribotest® legionella; urinary antigen test.
Copyright © 2024, Murakami et al.
Conflict of interest statement
Human subjects: Consent for treatment and open access publication was obtained or waived by all participants in this study. Conflicts of interest: In compliance with the ICMJE uniform disclosure form, all authors declare the following: Payment/services info: All authors have declared that no financial support was received from any organization for the submitted work. Financial relationships: All authors have declared that they have no financial relationships at present or within the previous three years with any organizations that might have an interest in the submitted work. Other relationships: All authors have declared that there are no other relationships or activities that could appear to have influenced the submitted work.
Figures
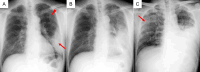
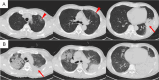

Similar articles
-
Severe Legionella Pneumonia in Which Serial Testing by Ribotest® Legionella was Useful for the Diagnosis.Intern Med. 2023 Oct 15;62(20):2989-2993. doi: 10.2169/internalmedicine.0766-22. Epub 2023 Mar 8. Intern Med. 2023. PMID: 36889700 Free PMC article.
-
Evaluation of five Legionella urinary antigen detection kits including new Ribotest Legionella for simultaneous detection of ribosomal protein L7/L12.J Infect Chemother. 2021 Oct;27(10):1533-1535. doi: 10.1016/j.jiac.2021.05.019. Epub 2021 Jun 2. J Infect Chemother. 2021. PMID: 34088604
-
A case of severe pneumonia caused by Legionella longbeachae with positive results by a Legionella urinary antigen detection kit.Ther Adv Infect Dis. 2023 Jun 14;10:20499361231179863. doi: 10.1177/20499361231179863. eCollection 2023 Jan-Dec. Ther Adv Infect Dis. 2023. PMID: 37363443 Free PMC article.
-
Legionella longbeachae pneumonia: A case report and literature review in Japan.J Infect Chemother. 2021 May;27(5):751-754. doi: 10.1016/j.jiac.2020.12.010. Epub 2021 Jan 2. J Infect Chemother. 2021. PMID: 33402302 Review.
-
Urinary Antigen Testing for Respiratory Infections: Current Perspectives on Utility and Limitations.Infect Drug Resist. 2022 Apr 27;15:2219-2228. doi: 10.2147/IDR.S321168. eCollection 2022. Infect Drug Resist. 2022. PMID: 35510157 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Diagnostic accuracy of urinary antigen tests for legionellosis: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Kawasaki T, Nakagawa N, Murata M, et al. Respir Investig. 2022;60:205–214. - PubMed
-
- Distribution of Legionella species and serogroups in patients with culture-confirmed Legionella pneumonia. Miyashita N, Higa F, Aoki Y, et al. J Infect Chemother. 2020;26:411–417. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
