Obesity and Sympathetic Overactivity in Young Individuals With Hypertension: Clinical Perspective of Indian Healthcare Providers
- PMID: 39712757
- PMCID: PMC11662092
- DOI: 10.7759/cureus.74115
Obesity and Sympathetic Overactivity in Young Individuals With Hypertension: Clinical Perspective of Indian Healthcare Providers
Abstract
Introduction: To understand the current clinical practices followed by healthcare professionals (HCPs) among populations with hypertension and obesity with sympathetic overactivity and develop strategies to improve the management of hypertension.
Methods: A standard questionnaire was formulated based on high sympathetic overactivity and/or obesity in young patients with hypertension to gather information on the perception and practices of HCPs toward the management of young patients with hypertension who have high sympathetic overactivity and/or obesity. HCPs throughout India were selected. The key insights and recommendations from the panel discussion were summarized in a report that helped to develop strategies to improve the management of young hypertension patients with high sympathetic overactivity/obesity.
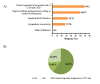
Results: A total of 1170 HCPs participated in the survey and in panel discussion meetings. According to 53% of HCPs, patients with hypertension with increased sympathetic overactivity or stress are most commonly aged 41-60 years. These patients have a higher likelihood of developing stroke (60%), alcoholism (46%), and sleep apnea (41%). Moreover, these HCPs also opined that patients with hypertension and obesity are at greater risk of developing coronary artery disease and chronic kidney disease (69%) and often require multiple antihypertensive drugs (60%). For the management of hypertension in obese patients with sympathetic overactivity, a combination of telmisartan and cardio-selective beta-blockers is the preferred treatment (66%). Additionally, a combination of telmisartan and metoprolol is recommended to control sympathetic overactivity in obese patients with hypertension.
Conclusion: Sympathetic overactivity is becoming more common in young adults with hypertension, and the combination of telmisartan and cardio-selective beta-blockers is the best treatment option for these patients. This approach may help to effectively manage hypertension and reduce the risk of complications associated with sympathetic overactivity. The limitation of the study is its reliance on self-reported data from HCPs, which may introduce bias.
Keywords: beta-blockers; coronary artery disease; hypertension; metoprolol; obesity; preventive effect; sympathetic overactivity; telmisartan.
Copyright © 2024, Jadhav et al.
Conflict of interest statement
Human subjects: Consent for treatment and open access publication was obtained or waived by all participants in this study. ACEAS Independent Ethics Committee issued approval NA. This study was conducted according to the Declaration of Helsinki principles and followed the guidelines for Good Epidemiology Practice. The ACEAS Independent Ethics Committee approved the study on 15 October 2022. Animal subjects: All authors have confirmed that this study did not involve animal subjects or tissue. Conflicts of interest: In compliance with the ICMJE uniform disclosure form, all authors declare the following: Payment/services info: This initiative was funded by USV Private Limited, Mumbai. Financial relationships: Dr. Santosh Revankar declare(s) employment from USV Private Limited, Mumbai. Amit Gupta declare(s) employment from USV Private Limited, Mumbai. Shweta Ghatge declare(s) employment from USV Private Limited, Mumbai. Other relationships: Amit Gupta, Shweta Ghatge, and Santosh Revankar are employees of USV Private Limited. All other authors have no conflicts of interest to declare.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Hypertension in Young Adults in India: Perspectives and Therapeutic Options amongst Clinician's in a Cross Sectional Observational Study.J Assoc Physicians India. 2021 Nov;69(11):11-12. J Assoc Physicians India. 2021. PMID: 34781615
-
Fixed-dose Combination of Metoprolol, Telmisartan, and Chlorthalidone for Essential Hypertension in Adults with Stable Coronary Artery Disease: Phase III Study.Adv Ther. 2022 Feb;39(2):923-942. doi: 10.1007/s12325-021-01971-9. Epub 2021 Dec 17. Adv Ther. 2022. PMID: 34918194 Clinical Trial.
-
Sympathetic overactivity in hypertension and cardiovascular disease.Curr Vasc Pharmacol. 2014 Jan;12(1):4-15. doi: 10.2174/15701611113119990140. Curr Vasc Pharmacol. 2014. PMID: 23905597 Review.
-
Position of Beta-blockers in the Treatment of Hypertension Today: An Indian Consensus.J Assoc Physicians India. 2024 Oct;72(10):83-90. doi: 10.59556/japi.72.0715. J Assoc Physicians India. 2024. PMID: 39390868
-
Sex differences in sympathetic activity in obesity and its related hypertension.Ann N Y Acad Sci. 2019 Oct;1454(1):31-41. doi: 10.1111/nyas.14095. Epub 2019 May 14. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 2019. PMID: 31087350 Review.
References
-
- National Center for Health Statistics. Hypertension prevalence, awareness, treatment, and control among adults age 18 and older: United States, August 2021-August 2023. 2024. https://www.cdc.gov/nchs/products/databriefs/db511.htm https://www.cdc.gov/nchs/products/databriefs/db511.htm
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources