Evaluation of Vinca Rosea's Protective Effects on Hepatic Function in Streptozotocin-Induced Diabetic Wistar Albino Rats
- PMID: 39712809
- PMCID: PMC11662991
- DOI: 10.7759/cureus.74166
Evaluation of Vinca Rosea's Protective Effects on Hepatic Function in Streptozotocin-Induced Diabetic Wistar Albino Rats
Abstract
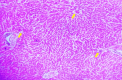
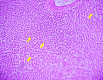
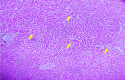
Background Diabetes mellitus, characterized by chronic hyperglycemia, often leads to severe hepatic dysfunction, including increased liver enzyme levels and histopathological changes in the liver. Streptozotocin (STZ)-induced diabetic rat models provide a valuable method for evaluating potential therapeutic agents that target hepatic complications. Vinca rosea, a medicinal plant with known anti-diabetic properties, has been used traditionally for its hepatoprotective effects, although scientific evidence is limited. Objective This study aimed to evaluate the protective effects of Vinca rosea leaf extract on hepatic function, including biochemical and histopathological changes, in STZ-induced diabetic Wistar albino rats. Methods Thirty male Wistar albino rats were randomly divided into five groups: Normal control (NC), diabetic control (DC), low-dose Vinca rosea (LD, 200 mg/kg), high-dose Vinca rosea (HD, 400 mg/kg), and positive control (PC, metformin 100 mg/kg). Diabetes was induced by a single intraperitoneal injection of STZ (100 mg/kg). Vinca rosea treatment was administered daily for 30 days. Blood samples were collected at 15 and 30 days to assess blood glucose and liver function, including serum bilirubin, aspartate aminotransferase (AST), and alanine aminotransferase (ALT) levels. Liver tissue was collected for histopathological examination. Data were analyzed using analysis of variance (ANOVA), with p < 0.05 considered statistically significant. Results The DC group showed significantly elevated blood glucose levels (256 ± 19.8 mg/dL at 15 days and 308.5 ± 13.1 mg/dL at 30 days). Vinca rosea treatment significantly reduced blood glucose in a dose-dependent manner, with the HD group showing the greatest improvement (143 ± 12.7 mg/dL at 15 days and 158.5 ± 10.7 mg/dL at 30 days). Liver function markers, including total and direct bilirubin, AST, and ALT, were significantly elevated in the DC group, indicating hepatic damage. Vinca rosea-treated groups showed significant improvements in all liver function parameters, with the HD group displaying the most substantial reductions in bilirubin, AST, and ALT levels. Histopathological analysis revealed marked hepatocellular damage in the DC group, including necrosis and ballooning degeneration. In contrast, Vinca rosea-treated groups, particularly the HD group, exhibited near-normal liver architecture with minimal damage. Conclusion Vinca rosea demonstrated significant hepatoprotective effects in STZ-induced diabetic rats by reducing blood glucose levels and improving liver function. These results suggest that Vinca rosea could be a promising therapeutic agent for managing diabetes-related hepatic dysfunction.
Keywords: alt; ast; diabetes; hepatic function; liver enzymes; serum bilirubin; stz; vinca rosea; wistar rats.
Copyright © 2024, Mallikarjuna Rao et al.
Conflict of interest statement
Human subjects: All authors have confirmed that this study did not involve human participants or tissue. Animal subjects: Roland Institute of Pharmaceutical Sciences, Berhampur Issued protocol number IEC/RIPS/2022/159. Conflicts of interest: In compliance with the ICMJE uniform disclosure form, all authors declare the following: Payment/services info: All authors have declared that no financial support was received from any organization for the submitted work. Financial relationships: All authors have declared that they have no financial relationships at present or within the previous three years with any organizations that might have an interest in the submitted work. Other relationships: All authors have declared that there are no other relationships or activities that could appear to have influenced the submitted work.
Figures


Similar articles
-
The Protective Effect of Hydroalcoholic Extract of Rosa canina (Dog Rose) Fruit on Liver Function and Structure in Streptozotocin-Induced Diabetes in Rats.J Diet Suppl. 2018 Sep 3;15(5):624-635. doi: 10.1080/19390211.2017.1369205. Epub 2017 Nov 2. J Diet Suppl. 2018. PMID: 29095652
-
Protective and antidiabetic effects of extract from Nigella sativa on blood glucose concentrations against streptozotocin (STZ)-induced diabetic in rats: an experimental study with histopathological evaluation.Diagn Pathol. 2013 Aug 15;8:137. doi: 10.1186/1746-1596-8-137. Diagn Pathol. 2013. Retraction in: Diagn Pathol. 2016 Nov 2;11(1):125. doi: 10.1186/s13000-016-0571-6. PMID: 23947821 Free PMC article. Retracted.
-
Effects of combined leaf extract of Vernonia amygdalina and Azadirachta indica on hepatic morphology and hepatotoxicity markers in streptozotocin-induced diabetic rats.Zhong Xi Yi Jie He Xue Bao. 2011 Dec;9(12):1373-9. doi: 10.3736/jcim20111215. Zhong Xi Yi Jie He Xue Bao. 2011. PMID: 22152778
-
Protective and hypoglycemic effects of celery seed on streptozotocin-induced diabetic rats: experimental and histopathological evaluation.Acta Diabetol. 2016 Aug;53(4):609-19. doi: 10.1007/s00592-016-0842-4. Epub 2016 Mar 4. Acta Diabetol. 2016. PMID: 26940333
-
Hepatoprotective, Antihyperlipidemic, and Anti-inflammatory Activity of Moringa oleifera in Diabetic-induced Damage in Male Wistar Rats.Pharmacognosy Res. 2017 Apr-Jun;9(2):182-187. doi: 10.4103/0974-8490.204651. Pharmacognosy Res. 2017. PMID: 28539743 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Diabetes mellitus: classification, mediators, and complications; a gate to identify potential targets for the development of new effective treatments. Antar SA, Ashour NA, Sharaky M, et al. Biomed Pharmacother. 2023;168:115734. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
