Increasing Trends in the Pancreatitis Risk With Tumor Necrosis Factor Inhibitor Use
- PMID: 39712842
- PMCID: PMC11663436
- DOI: 10.7759/cureus.74245
Increasing Trends in the Pancreatitis Risk With Tumor Necrosis Factor Inhibitor Use
Abstract
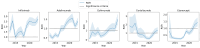
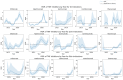
Tumor necrosis factor (TNF) inhibitors are a class of pharmacologic agents used to treat a wide range of immunologic diseases. We present a systematic study of the pancreatitis risk with TNF inhibitor use through a retrospective case-control design disproportionality analysis of the U.S. Food and Drug Administration Adverse Event Reporting System (FAERS) database, with data ranging from the fourth quarter of 2012 (2012 Q4) to the second quarter of 2024 (2024 Q2). Our analysis reveals an increasing trend in the pancreatitis risk with TNF inhibitors when stratified by year, with all of the TNF inhibitors studied exhibiting significant association with pancreatitis in the year 2023. Furthermore, these results hold even when controlling for sex, age, concurrent use of azathioprine, and the indication for treatment. Our findings flag the necessity for a careful investigation and monitoring of pancreatitis risk in patients undergoing TNF inhibitor therapy, especially in recent years.
Keywords: disproportionality analysis; food and drug administration adverse event reporting system (faers); medication-induced pancreatitis; pharmacovigilance; tnf alpha inhibitor.
Copyright © 2024, Gu et al.
Conflict of interest statement
Human subjects: Consent for treatment and open access publication was obtained or waived by all participants in this study. Animal subjects: All authors have confirmed that this study did not involve animal subjects or tissue. Conflicts of interest: In compliance with the ICMJE uniform disclosure form, all authors declare the following: Payment/services info: All authors have declared that no financial support was received from any organization for the submitted work. Financial relationships: All authors have declared that they have no financial relationships at present or within the previous three years with any organizations that might have an interest in the submitted work. Other relationships: All authors have declared that there are no other relationships or activities that could appear to have influenced the submitted work.
Figures

References
-
- Tumor necrosis factor antagonist mechanisms of action: a comprehensive review. Tracey D, Klareskog L, Sasso EH, Salfeld JG, Tak PP. Pharmacol Ther. 2008;117:244–279. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
