Knowledge‑map Analysis of Ureteroscopy for Urolithiasis
- PMID: 39712886
- PMCID: PMC11662923
- DOI: 10.2147/JMDH.S493581
Knowledge‑map Analysis of Ureteroscopy for Urolithiasis
Abstract
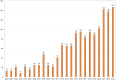
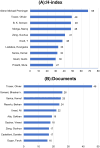
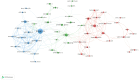
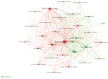
The utilization of ureteroscopy (URS) for managing urolithiasis has garnered substantial global recognition. Nonetheless, bibliometric analyses focusing on URS in the context of urolithiasis treatment remain sparse. Therefore, we used bibliometrics to summarize the relevant literature in this field in recent years, in order to grasp the core research directions, capture the developmental frontiers, and provide valuable information for urologists to understand the research hotspots. In this study, we compiled the literature on URS and urinary stones from the Web of Science core database over the past two decades. In this study, we compiled literature about URS and urolithiasis from the Web of Science Core Collection spanning the past two decades. The assembled data were subsequently visualized and analyzed using CiteSpace and VOSviewer software. The findings revealed a total of 1,461 publications, with a consistent annual increase and a notable surge post-2010. The most frequently occurring keywords identified were "ureteroscopy" and "calculi". Olivier Traxer, a prominent figure from France, is recognized as a leading expert in the domain, particularly emphasizing the practical application of diverse techniques for the treatment and management of urinary stones. The Journal of Urology has disseminated the most pertinent literature in this area, with Turkey emerging as the most prolific contributor. Keyword analysis within this field has identified four primary research hotspots: the investigation of complications to mitigate treatment risks, the standardization of treatment protocols, the determination of treatment indications based on stone types, and the implementation of novel techniques in ureteroscopic lithotripsy.
Keywords: bibliometric analysis; co-citation; ureteroscopy; urolithiasis; visual analysis.
© 2024 Guo et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Figures

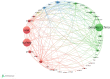

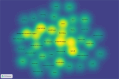
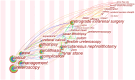
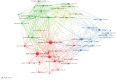
Similar articles
-
Knowledge-map analysis of percutaneous nephrolithotomy (PNL) for urolithiasis.Urolithiasis. 2023 Jan 20;51(1):34. doi: 10.1007/s00240-023-01406-w. Urolithiasis. 2023. PMID: 36662293 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Research trends and frontiers on risk factors of urinary stones: a bibliometric analysis from 2010 to 2023.Ren Fail. 2024 Dec;46(2):2440513. doi: 10.1080/0886022X.2024.2440513. Epub 2024 Dec 16. Ren Fail. 2024. PMID: 39681478 Free PMC article.
-
Ureteroscopy and Shock Wave Lithotripsy Trends from 2012 to 2019 Within the US Medicare Dataset: Sharp Growth in Ureteroscopy Utilization.J Endourol. 2023 Feb;37(2):219-224. doi: 10.1089/end.2022.0402. Epub 2022 Nov 3. J Endourol. 2023. PMID: 36205599
-
Bibliometric and visualized analysis on global trends and hotspots of TAK1 in regulated cell death: 1999 to 2024.Front Immunol. 2024 Oct 15;15:1437570. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2024.1437570. eCollection 2024. Front Immunol. 2024. PMID: 39474417 Free PMC article.
-
Analyzing global research trends and focal points in the utilization of laser techniques for the treatment of urolithiasis from 1978 to 2022: visualization and bibliometric analysis.Urolithiasis. 2024 Apr 17;52(1):67. doi: 10.1007/s00240-024-01568-1. Urolithiasis. 2024. PMID: 38630266 Review.
References
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

